Botany Units Cells – Chapter 7 Photosynthesis – Chapter 8 Plant
advertisement

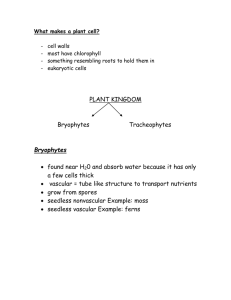
Botany Units 1. Cells – Chapter 7 2. Photosynthesis – Chapter 8 3. Plant Divisions – Chapter 22 4. Plant Characteristics – Chapter 22 5. Plant Reproduction – Chapters 22 and 24 6. Plant Structures (Roots, Stems, and Leaves) – Chapter 23 7. Plant Responses and Adaptations – Chapter 25 8. Plant Genetics – Chapter 11 Unit 1: Cells (Chapter 7) Vocabulary 1. Organelle 2. Cell 3. Prokaryote 4. Eukaryote 5. Cell wall 6. Cellulose 7. Cell membrane 8. Cytoplasm (cytosol) 9. Nucleus 10. Nucleolus 11. DNA 12. Vacuole 13. Ribosome 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. Golgi apparatus Endoplasmic reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplast Homeostasis Concentration Osmosis Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic Plasmolysis Flaccid Turgor I Can Statements: 1. What is a cell? 2. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ? 3. What type of cell are bacteria, animal cells, and plant cells? 4. What organelles do plant cells contain? 5. What are the functions of cell wall and cell membrane? 6. What is contained within the cytoplasm? 7. How does the nucleus control all cell functions? 8. What is the function of the ribosomes? 9. What are the differences in structure and functions of the smooth ER and rough ER? 10. Explain how the ribosomes, rough ER, smooth ER, and Golgi apparatus work together to create products for the cell. 11. Explain the similarities and differences between mitochondria and chloroplast. 12. What is homeostasis? 13. Explain the different types of solution concentrations. 14. What happens to the plant cell within each type of solution? Unit 2: Photosynthesis (Chapter 8) Vocabulary: 1. Reactants 2. Products 3. Cellular respiration 4. Photosynthesis 5. Autotroph 6. Heterotroph 7. Light–dependent reactions 8. Calvin cycle 9. Carbon fixation 10. Electron transport chain 11. ATP synthase 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. NADP+ ATP Glucose Photosystem Thylakoid Stroma Chlorophyll Pigment Mesophyll Stomata Transpiration I Can Statements: 1. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? 2. What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration? 3. What is ATP? 4. How does ATP store and release energy within the cell? 5. What is NADP+, and how does it function? 6. What is the thylakoid? 7. What are the two stages of photosynthesis? 8. Where does each stage of photosynthesis occur? 9. What is the function of chlorophyll? 10. Explain the steps of the light–dependent reactions. 11. What roles do the photosystems play in the light–dependent reactions? 12. Explain the electron transport chain. 13. How do the products of the light–dependent reactions feed into the Calvin cycle? 14. Explain the process of carbon fixation. 15. How do plants exchange gases? 16. What is transpiration? 17. What are the steps of the Calvin cycle? 18. How do plants use the products of the Calvin cycle? 19. What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis? Unit 3: Plant Divisions (Chapter 22) Vocabulary: 1. division 2. bryophytes 3. tracheophytes 4. gymnosperm 5. angiosperm 6. monocot 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. dicot vascular tissue spore seed cone flower I Can Statement: 1. What plants first evolved to land? 2. What are the 3 divisions of nonvascular plants? 3. How are nonvascular plants and seedless vascular plants similar? 4. What are the 4 divisions of seedless vascular plants? 5. Explain how vascular tissue caused plants to evolve. 6. How do seedless vascular plants and seed–bearing plants differ? 7. How does the production of seeds further evolve plants? 8. What are the 2 groups of seed–bearing plants? 9. Explain the difference in the 2 groups of seed–bearing plants? 10. What are the 4 divisions of gymnosperms? 11. What is a cone? 12. What division do all angiosperm belong to? 13. What are the 2 types of flowering plants? 14. What is a flower? Unit 4: Plant Characteristics (Chapter 22) Vocabulary: 1. gametophyte 2. sporophyte 3. alternation of generations 4. rhizoids 5. rhizomes 6. fronds 7. fiddleheads 8. lignin 9. tracheids 10. xylem 11. phloem 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. stem root leaf veins cotyledon annual biennial perennial herbaceous woody I Can Statements: 1. What are the basic plant characteristics? 2. What are the requirements of all plants? 3. What is a gametophyte? 4. What is a sporophyte? 5. Briefly explain alternation of generations. 6. Where did plants evolve from? 7. What are the basic structures of the bryophytes? 8. What is the dominant life cycle stage in bryophytes? 9. What are xylem and phloem? 10. What are the basic functions of roots, leaves, and stems? 11. Explain the basic structures of the seedless vascular plants. 12. What is the dominant life cycle stage in vascular plants? 13. How did the development of seeds increase the variations in plants? 14. What are some basic characteristics of gymnosperms? 15. How did flowers and fruits increase seed dispersal in angiosperms? 16. What are the major differences in monocots and dicots? 17. Explain the difference in herbaceous and woody plants. 18. What are annuals, biennials, and perennials? Unit 5: Plant Reproduction (Chapters 22 and 24) Vocabulary: 1. sexual reproduction 2. asexual reproduction 3. vegetative reproduction 4. budding 5. haploid 6. diploid 7. protonema 8. germination 9. gamete 10. antheridium 11. archegonium 12. sporangium 13. sori 14. pollen grain 15. pollination 16. pine cone 17. seed cone 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. ovules fertilization zygote embryo seed coat endosperm sepals petals stamen filament anther carpel (pistil) ovary style stigma fruit stolons I Can Statements: 1. What is alternation of generations? 2. How do the sporophyte and gametophyte life stages differ? 3. Which life stage is haploid or diploid? 4. Explain the process of bryophyte reproduction. 5. How do antheridium and archegonium differ? 6. What is required for a spore to germinate? 7. How do seedless vascular plants reproduce? 8. What differences are present between nonvascular and seedless vascular plant reproduction? 9. How do the gametophyte and sporophyte structures change as plant evolved? 10. Explain the structure of a seed. 11. What are the major reproductive stages of gymnosperms? 12. How does pollination within gymnosperms take place? 13. Explain the development of seeds in gymnosperms. 14. What is the function of a flower? 15. Explain each part of a flower. 16. How does pollination occur within angiosperms? 17. Explain the process of fertilization in flowering plants. 18. How does a seed develop in a flower? 19. Describe the differences in spores and seeds. 20. Explain how fruits develop. 21. How does a fruit increase the distance of seed dispersal? 22. What is required for a seed to germinate? 23. What is the difference in asexual and sexual reproduction? 24. Explain vegetative reproduction. Unit 6: Plant Structures – Roots, Stems, and Leaves (Chapter 23) Vocabulary: 1. differentiation 2. meristematic tissue 3. dermal tissue 4. ground tissue 5. taproot 6. fibrous roots 7. root hair 8. cortex 9. endodermis 10. vascular cylinder 11. root cap 12. node 13. internode 14. bud 15. vascular bundle 16. pith 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. I Can Statements: 1. What are the major organs of plants? 2. What are the basic functions of roots, stems, and leaves? 3. Explain differentiation. 4. Where is meristematic tissues found? 5. What are the dermal, vascular, and ground tissues? 6. How do the taproot and fibrous root systems differ? 7. Explain the structures of a root. 8. What are the major root functions? 9. Explain the structures of a stem. 10. What are the major functions of stems? 11. Explain the differences in monocot and dicot stems. 12. What is primary growth, and where does it occur? 13. What is the purpose of secondary growth? 14. How does vascular cambium and cork cambium differ? 15. What is the cortex? 16. What is the pith? 17. Explain heartwood and sapwood. 18. What is the function of bark? 19. What are the major functions of leaves? 20. Explain the structures within a leaf. 21. Why is the mesophyll important within the leaf? 22. What factors affect transpiration? 23. What controls the stomata? cambium (vascular, cork) primary growth secondary growth heartwood sapwood bark blade petiole palisade mesophyll spongy mesophyll cuticle guard cells epidermis epidermal cells meristem apical meristem Unit 7: Plant Responses and Adaptations (Chapter 25) Vocabulary: 1. adaptation 2. hormone 3. herbicide 4. insecticide 5. toxin 6. urushiol 7. nectar 8. parasite 9. host 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. dormancy adventitious roots prop roots tropisms phototropism gravitropism thigmotropism xerophytes epiphyte I Can Statements: 1. How does a plant know when to grow? 2. What is a hormone? 3. What are the 3 major types of tropisms? 4. Explain phototropism. 5. What is gravitropism? 6. How do herbicides affect plant growth? 7. What is thigmotropism? 8. Explain dormancy of plants and seeds. 9. What is an adaptation? 10. How have aquatic plants adapted to living in water? 11. Explain the adaptations of xerophytes. 12. How have carnivorous plants adapted to live in their habitats? 13. Explain epiphyte adaptations. 14. What chemical defenses do some plants possess? 15. What is urushiol? 16. What may the toxins of plants cause? 17. List and explain the common leaf adaptations. 18. What are adventitious roots and prop roots? 19. What are some common stem modifications used for storage and dormancy? 20. Why do seeds have adaptations? 21. Why are there different flower sizes, shapes and smells? Unit 8: Plant Genetics (Chapter 11) Vocabulary: 1. Gregor Mendel 2. genetics 3. heredity 4. gene 5. trait 6. allele 7. P generation 8. F1 generation 9. true–breeding 10. hybrid 11. homozygous 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. heterozygous genotype phenotype dominant recessive Punnett square monohybrid cross probability segregation incomplete dominance codominance I Can Statements: 1. Who is Gregor Mendel? 2. What is genetics and heredity? 3. What type of plant did Mendel use to perform his experiments? 4. How do genes, traits, and alleles differ? 5. Explain dominant alleles and recessive alleles. 6. How are dominant and recessive alleles represented? 7. What is a true–breeding plant? 8. What is a hybrid? 9. Explain the P generation and the F1 generation. 10. How do homozygous and heterozygous individuals differ? 11. What is the process of segregation? 12. What do genotype and phenotype represent? 13. Explain the purpose of a Punnett square. 14. How is probability calculated? 15. What is a monohybrid cross? 16. Explain incomplete dominance. 17. What is codominance? 18. How does the environment affect genetics?