Chapter: Nature of Science Scientific inquiry and steps Branches of
advertisement

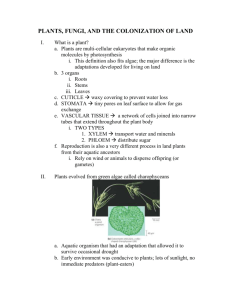
Chapter: Nature of Science Scientific inquiry and steps Branches of science Theory vs. law Scientific tools Precision vs accuracy significant digits Chapter 1: Classifying Life Characteristics of life Needs of all living things Classification System Aristotle Carolus Linnaeus binomial nomenclature genus species Domains Archaea Eubacteria Eukaryota Classification tools dichotomous keys cladograms field guides Development of microscopes Robert Hook Anton Van Leeuwenhoek Types of microscopes light compound electron transmission scanning Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Function Cell Theory contributors Hook, Schwann, Schleiden, & Virchow Macromolecules carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic acids Water structure importance Cell parts and functions Animal vs Plant cell Prokaryote vs eukaryote Transport of materials into/out of the cell and examples of substances that would require these Passive transport diffusion osmosis facilitated diffusion carrier proteins channel proteins Active transport active transport endocytosis exocytosis Cellular respiration glycolysis reaction location of reaction results of reaction Fermentation glycolysis reaction does it proceed? Which is more beneficial – respiration or fermentation and why? Photosynthesis reaction location of reaction importance of reaction Chapter 3: From Cell to Organism cell cycle phases length of cycle and types of cells importance of cell division mitosis stages results cytokinesis levels of organization atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism unicellular prokaryotes eukaryotes multicellular cell differentiation stem cells Chapter 4: Reproduction of organisms sexual reproduction egg sperm zygote fertilization advantages and disadvantages of …. diploid vs haploid cells chromosomes homologous pairs meiosis and steps meiosis I meiosis II importance of process compare and contrast mitosis vs meiosis asexual reproduction binary fission budding regeneration vegetative reproduction cloning advantages and disadvantages of…. Chapter 5: Genetics genetics heredity Mendel and experiments true-breeding = self pollinating cross pollination first generation results second generation=hybrid results conclusions of experiments dominant trait recessive trait genes vs alleles phenotype & genotype homozygous vs heterozygous Punnett squares probability/ratios pedigrees & importance complex patterns of inheritance dominance incomplete dominance codominance multiple alleles blood type polygenic inheritance hair, skin, eye color environmental effects on heredity DNA double helix components = nucleotides phosphate group deoxyribose nitrogen base adenine cytosine guanine thymine replication location transcription location mRNA difference from DNA function translation rRNA & tRNA’s role/function location mutations deletion substitution invertion results of mutations Chapter 6: The Environment and Changes Over Time fossil different formation methods relative dating vs absolute dating geologic time scale extinction sudden vs gradual changes Charles Darwin Natural Selection Theory steps in theory reproduction variations competition selection Adaptations structural behavioral functional environmental influence camouflage vs mimicry artificial selection selective breeding evidence of evolution fossil record homologous structures vestigial structures embryology importance of pharyngeal pouches DNA divergence from common ancestor Chapter 7: Bacteria & Viruses bacteria prokaryotic cell Archaea or Eubacteria structural features capsule pilli flagella in some plasmids cytoplasm ribosomes cell membrane cell wall gram positive vs gram negative cocci, bacillus, spirilla anaerobic vs aerobic hetrotrophic vs autotrophic binary fission conjugation endospore beneficial bacteria cyanobacteria – autotrophic phytoplankton decomposition nitrogen fixing bioremediation food production harmful bacteria = pathogen diseases antibiotics resistance development food poisoning pasteurization viruses nonliving lytic vs lysogenic cycles specific target cells mutation rate viral diseases flu; AIDS methods of prevention vaccines natural immunity good hygiene practices…. “CLOUD” gene therapy Chapter 8: Protists and Fungi Kingdom Protista – “misfit organisms” classification animal-like = “protozoan”; heterotrophic classified by method of movement ciliates Paramecium flagellates Euglena – if no light for photosynthesis sarcodine Amoeba pseudopods importance of protozoans plant-like = “algae”; autotrophic diatoms dinoflagellates Bioluminescent Bay, Puerto Rico euglenoids preferred category eye spot algae unicellular multicellular green brown red importance of plant-like protists fungus-like slime molds water mold Great Irish Potato Famine importance of … Kingdom Fungi structure mycelium hyphae fruiting body cell wall = chitin spores classified by sexual reproductive structure club fungi basidium Example = button mushrooms (like the ones on a pizza) sac fungi ascus ascospores Example = yeast zygote fungi zygosporangia zygospores Example = bread mold imperfect fungi no observable sexual reproductive structure Example = Penicillium athlete’s foot fungus importance of fungi saprophyte mycorrhizae – symbiotic relationship health & medicine lichens symbiotic relationship between fungi and cyanobacteria or green algae bioindicators of environment food source for herbivores Chapter 9: Plants autotrophic eukaryotic multicellular characteristics unique to plants cell wall = cellulose chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll central vacuole adaptations for land cuticle cellulose and lignin in cell wall vascular tissue xylem phloem cambium reproduction evolution of seeds plant classification nonvascular rely on osmosis/diffusion seedless rely on spores mosses liverworts hornworts vascular seedless ferns club mosses horsetails seed true stems, leaves, roots gymnosperm – “cone bearing” or “naked seed” oldest plants needle-like or scale-like leaves conifers cycads ginkgoes gnetophytes angiosperm – flowering plants seeds in fruit monocotyledon vs dicotyledon annuals biennials perennials importance of each group leaves in vascular seed plants layers and role in photosynthesis Chapter 10: Plant Processes and Reproduction photosynthesis vs cellular respiration in plants tropisms phototropism gravitropism/geotropism thigmotropism photoperiodism long-day short-day day-neutral plant hormones auxins gibberellins ethylene cytokinins absicsic acid alternation of generations = plant life cycle/generation sporophyte = diploid fertilization initiates sporophyte stage gametophyte = haploid meiosis initiates gametophyte stage Moss life cycle = typical of nonvascular seedless plants gametophyte = most prevalent stage; autotrophic; separate male & female plants sporophyte – brown stalks; nonphotosythetic – relies on gametophyte for energy Fern life cycle = typical of vascular seedless plants sporophyte = most prevalent stage; photosynthetic sori produce spores gametophyte = prothallus microscopic heart-shaped structure contains both male & female reproducing cells Seed Plants pollination gymnosperm pollen in smaller male cones ovule in larger female cones seed embryo seed coat endosperm = nutrient/food supply angiosperm flower parts flower becomes fruit with seeds inside seed dispersal methods