File - Mr. Bird's Chemistry Page
advertisement

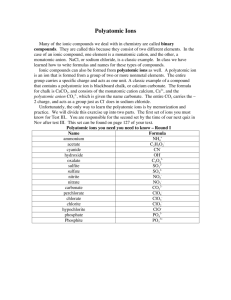
Name: _________________________________________________________________ AP Chemistry AP Chemistry I hope you are excited about taking in AP Chemistry for this year. The difference between this class and your 1st year chemistry course is so significant; you must be prepared to work like you never have before. Based on the statistics from the College Board, this is one of the most challenging courses at Rangeview. You must have successful grades in honors math courses and your 1st year of chemistry in order to perform the way your teachers think you can. You should feel honored to be part of this elite group that will attempt to explain how all matter is manipulated in our universe. If you are ready for the demands of the course, you are expected to complete this summer assignment so that we can get the most 3’s, 4’s, and 5’s ever seen by an AP class. Thank you, Mr. Bird mabird@aps.k12.co.us AP Chemistry Assignment: In this assignment, you will be mastering the details of what you learned from your first year in chemistry. You will need to solve some problems from the first three chapters of the textbook. I have posted the Power Point presentations that accompany our book along with the sample problems from each chapter that show you how to solve the problems. You must memorize element names, polyatomic ions, measurement conversion factors. You will be tested on the assignments on your return. You will be required to use the course website to complete some of the assignments and it will also be used for support throughout the summer. The summer assignment can be found at www.sciencebird.weebly.com Assignments: 1. Make flash cards for memorization. a. Use index cards, not cut strips of paper to produce your flash cards. You will need flash cards of the following: i. Metric Units ii. Element Names and Symbols iii. Polyatomic Ions You will see a list of what needs to be on the flash cards in this packet. For elements and ions, put the symbol on one side and the name on the other. Have only one element or ion per card. You will be given a grade for these flash cards on your return from summer and be tested on them throughout the year. You can visit the summer assignment webpage to learn these elements, ions, and metric prefixes from quizlet.com, an online resource for playing games to memorize content. You can even use your iPod to play games for memorization. 2. View Podcasts and Complete Assignments on the Early Chapters (Review from Chem yr1) Directions: Go to Mr. Barron’s (a former RHS AP Chem teacher) YouTube channel at http://www.youtube.com/user/awbarron/videos. Resources for completing the assignments: Following this page are most of the resources you will need to complete the assignment over summer. You will need to access the course webpage for some of the assignments, but most of what you need is attached here in this packet. If you have any technical problems over the summer with the website, email Mr. Bird with your question. Name: _________________________________________________________________ AP Chemistry Metric Unit Flashcards Directions: Write the unit name and quantity on one side and the symbol on the other. Example Flashcard: Length, meter Quantity Length Mass Volume Temperature Time Energy Amount of a Substance m Unit Meter Gram Liter Celsius Seconds Joule Symbol m g L °C s J Mole mol Metric Prefixes and Conversion Factor Flashcards Directions: Write the unit name and quantity on one side and the symbol on the other. Example Flashcard: Kilo Prefix Kilo- (k__) BASE UNIT deci- (d__) centi- (c__) milli- (m__) micro- (µ__) nano- (n__) Example Conversion: Given: 5kL = ? L Formula: 1000L = 1kL Work: 5kL× 1000L 1kL =5000L 1 kilo = 1000 base unit Conversion Factors 1k__ = 1000 base unit (Example: There are 1000 meters in a kilometer.) The main metric unit (meter (m), liter (L), gram (g), etc.) 10 d__ = 1 base unit (Example: There are 10 decimeters in a meter) 100 c__ = 1 base unit (Example: There are 100 centimeters in a meter) 1000 m__ = 1 base unit (Example: There are 1000 millimeters in a meter) 1 x 106 µ__ = 1 base unit (Example: There are 1 x 106 micrometers in a meter) 1 x 109 n__ = 1 base unit (Example: There are 1 x 109 nanometers in a meter) Name: _________________________________________________________________ AP Chemistry Element Flashcards Directions: Write the element symbol on one side and the name on the other. Example Flashcard: Gallium Aluminum Argon Barium Beryllium Bismuth Boron Bromine Calcium Carbon Cesium Chlorine Chromium Cobalt Copper Fluorine Gold Helium Al Ar Ba Be Bi B Br Ca C Cs Cl Cr Co Cu F Au He Gallium Germanium Hydrogen Iodine Iron Lead Lithium Magnesium Manganese Mercury Neon Nickel Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorous Platinum Potassium Ga Ga Ge H I Fe Pb Li Mg Mn Hg Ne Ni N O P Pt K Radon Rubidium Scandium Silicon Silver Sodium Strontium Sulfur Titanium Tin Uranium Xenon Zinc Rn Rb Sc Si Ag Na Sr S Ti Sn U Xe Zn Memorization Hints: Elements/Symbols Silver Ag If a person who is expecting a present of a gold necklace and receives a silver one. He might say, “Ag, I didn’t want silver” “Hey you, I want that gold necklace!” Said with a “Hey you” sounding like Au. Gold Au That brother of mine – Bro of mine! Bromine Br “Caws give milk!” Pronounced with an accent to make cows sound like it’s spelled Calcium Ca with an A. “You can Clean with chlorine!” Chlorine Cl “Fe, Fi, Fo, Fum, I’m an iron man!” Iron Fe If you breathe in helium, you will laugh. He, He, He! Helium He Greek mythology – Hg stands for Helmet guy! Mercury Hg You will get Kicked out of school for the double nasty! You can’t do the first three Potassium K letters and cannot say the next three! “Naw, I don’t way any sodium!” Sodium Na “Nick owes me a nickel!” Nickel Ni “Open your mouth wide to take in oxygen!” Oxygen O Pencil broke! Lead Pb Silly con! Silicon Si A tin roof gets hot in the Sun. Tin Sn Take the first three letters - Man Manganese Mn Take the first three letters - Mag Magnesium Mg Name: _________________________________________________________________ AP Chemistry Polyatomic Ion Flashcards Directions: Write the polyatomic ion symbol on one side and the name on the other. Example Flashcard: CN- cyanide Polyatomic ions are groups of multiple atoms that have a charge (positive or negative). The symbols shown below tell you what elements are in the ion, how many atoms of each, and the charge. For example, NO− 3 contains a nitrogen atom, four hydrogen atoms, and the entire group has a charge of -1. Memorization Hints: Polyatomic Ions If you have two ions with similar names and the only difference is the number of oxygen atoms in your ion: -ite means smaller number of O -ate means larger number of O Hypo- (smallest) and Per- (largest) are used if there are four ions with similar names and different numbers of oxygen. Positive Polyatomic Ions (Polyatomic Cations) 1+ Ammonium (NH4 +) Negative Polyatomic Ions (Polyatomic Anions) 1Acetate (C2H3O2-) Chlorate (ClO3-) Chlorite (ClO2-) Cyanide (CN-) Dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4-) Hydrogen Carbonate or bicarbonate (HCO3-) Hydrogen Sulfite or bisulfite (HSO3-) Hydroxide (OH-) Nitrate (NO3-) Nitrite (NO2-) Perchlorate (ClO4-) Permanganate (MnO4-) Thiocyanate (SCN-) 2Carbonate (CO32-) Chromate (CrO42-) Dichromate (Cr2O7 2- ) Hydrogen Phosphate (HPO4 2- ) Oxalate (C2O42-) Peroxide (O2 2- ) Sulfate (SO4 2- ) Sulfite (SO3 2- ) 3Arsenate (AsO4 3- ) Phosphate (PO4 3- )