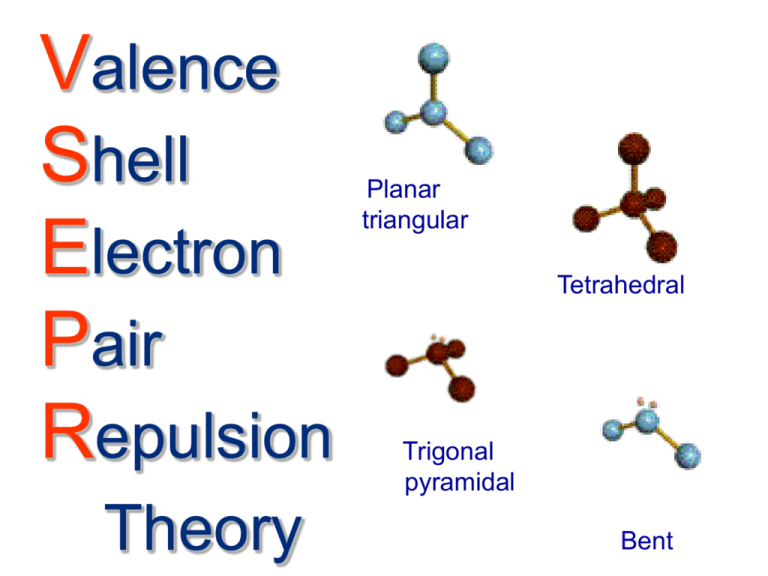
Valence
Shell
Electron
Pair
Repulsion
Theory
Planar
triangular
Tetrahedral
Trigonal
pyramidal
Bent
Molecular Shape
VSEPR theory assumes that the shape of a
molecule is determined by the repulsion of
electron pairs.
VSEPR Theory
• Based on Electron Dot (Lewis structures)
• Theory predicts shapes of compounds
• abbreviated VSEPR
• VSEPR (pronounced “vesper”) stands for
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
• VSEPR predicts shapes based on electron pairs
repelling (in bonds or by themselves)
• Electrons around central nucleus
repel each other. So, structures
have atoms maximally spread out
VSEPR overview
• Each shape has a name
(you will have to know these)
• Names of Shapes:
• tetrahedral
• trigonal pyramidal
• Bent
• Linear
• trigonal planar
Models
Tetrahedral
Triangular Planar
Trigonal pyramidal
Bent or V
Linear
methane, CH4
Tetrahedral
109.5°
Bonds are all evenly spaced electrons
..
..
..
..
ammonia
NH3
Trigonal
Pyramidal
Less repulsion between the bonding pairs of electrons
..
..
..
water, H2O
109.5° (109.5°) 109.5° (107°)
109.5° (104.5°)
..
..
..
Bent or V
2 unshared pairs of e’s
at top of O repel bonds
and force them to bend
Molecule
CH4
Lewis Structure
Number of
electron pairs
SHAPE
4
Tetrahedral
NH3
4
Trigonal
Pyramidal
(3 shared
1 lone pair)
Molecule
H2O
Lewis Structure
Number of
electron pairs
Bent or V
4
(2 shared
2 lone pairs)
Linear
CO2
SHAPE
2
Molecule
BeCl2
BF3
Lewis Structure
Number of
electron pairs
2
3
SHAPE
Linear
Trigonal
Planar
HYBRIDIZATION
Hybridization – mixing of two or more atomic
orbitals to form a new set of hybrid orbitals.
1. Mix at least 2 nonequivalent atomic orbitals (e.g. s
and p). Hybrid orbitals have very different shape
from original atomic orbitals.
2. Number of hybrid orbitals is equal to number of
pure atomic orbitals used in the hybridization
process.
3. Covalent bonds are formed by:
a. Overlap of hybrid orbitals with atomic orbitals
b. Overlap of hybrid orbitals with other hybrid
orbitals
10.4
3
sp
Hybridization
• Combination of one s and three p orbitals.
• Tetrahedral – or 4 equal “attachments”
• Remember: 1 bond has 2 electrons…..and 1 lone pair
has 2 electrons. Therefore, they are equal.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
16
The Formation of sp3 Hybrid
Orbitals
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
17
Tetrahedral Set of Four sp3
Orbitals
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
18
2
sp
Hybridization
• Combination of one s and two p orbitals.
• Trigonal Planer – 3 equal attachments.
• One p orbital is not used.
Oriented perpendicular to the plane of the sp2
orbitals.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
19
Sigma () Bond
• Electron pair is shared in an area centered on a line
running between the atoms.
• SINGLE BOND
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
20
Pi () Bond
• Forms double and triple bonds by sharing electron
pair(s) in the space above and below the σ bond.
• Uses the unhybridized p orbitals.
• DOUBLE OR TRIPLE BOND
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
21
sp Hybridization
• Combination of one s and one p orbital.
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
22
When One s Orbital and One p Orbital are Hybridized, a Set of Two sp
Orbitals Oriented at 180 Degrees Results
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
23
The Orbitals for CO2
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
24
3
sp d
Hybridization
• Combination of one d, one s, and three p orbitals.
• Gives a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement of five
equivalent hybrid orbitals.
• Recently disproven
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
25
The Orbitals Used to Form the
Bonds in PCl5
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
26
3
2
sp d
Hybridization
• Combination of two d, one s, and three p orbitals.
• Gives an octahedral arrangement of six equivalent
hybrid orbitals.
• Recently disproven
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
27
How is the Xenon Atom in XeF4
Hybridized?
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
28
Concept Check
Draw the Lewis structure for HCN.
Which hybrid orbitals are used?
Draw HCN:
Showing all bonds between atoms.
Labeling each bond as or .
Copyright © Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
29