Hands-On Chromatography
advertisement

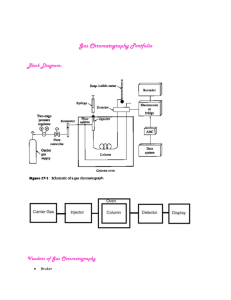
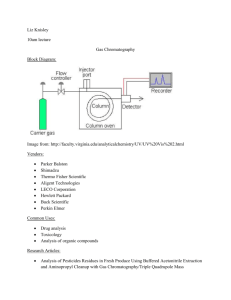
Hands-on Chromatography Sheryl K. Hoffmann Concordia College CONASTA 60 Definitions Definition 1: Chromatography is a technique for separating similar compounds from one another by using differences in the strength of their adsorption on an inert material. Adsorb: hold (molecules of a gas or liquid or solute) to its surface Absorb: swallow up, incorporate, take in Definition 2: Chromatography is a technique which can be used to separate the components of a mixture. The method depends upon differences in the abilities of the components to adhere to a porus solid such as silica gel, called the stationary phase differences in the abilities of the components to be dissolved in a stream of liquid or gas, called the mobile phase, which is passed over the solid. Main Types Paper Chromatography Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) Column Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Gas-Liquid Chromatography Basic Method Spotting Technique Tips If the spot is large, components start from different origins and will thus blur any separation that would normally occur. Try a quick dabbing motion, the longer the liquid is in contact with the paper the larger the spot If the spot is not very concentrated the resulting bands, once spread over a wider area, will be even fainter. If the solution to be spotted is not very strong, spot several times, being sure to allow the spot to dry inbetween, a hair drier will speed up the drying process. Hands On Activities 1. Practice Spotting 2. Comparison of 1M NaCl & Water in Separating Food Colour 3. Sticks of Chalk 4. Counterfeit Smarties? 5. Comparing Black Inks Activity 2 – Food Dyes Activity 3 - Chalk Activity 4 - Smarties Activity 5 – Black Pen Ink Activity 6 – Geranium TLC Paper Activity 6A – Frozen Spinach Activity 6A –Spinach Activity 7 – 2 Columns