9-Fluorenone Reduction: Lab Experiment & Analysis
advertisement

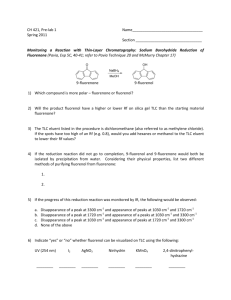
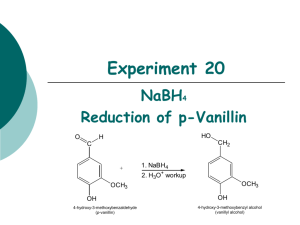
Experiment 20: REDUCTION OF 9-FLUORENONE 1. NaBH4 2. H3O+ O OH Objectives: To synthesize a secondary alcohol from a ketone using a sodium borohydride reduction. To purify and isolate the product using recrystallization. To analyze the purity of the product using TLC, HPLC and melting point analysis. To characterize the reactants and products using NMR spectroscopy. Before coming to lab… Review these techniques: Fractional distillation Vacuum filtration GC Analysis REDUCTION USING NaBH4 NaBH4 (sodium borohydride) is a versatile and useful reducing agent in organic chemistry. A reducing agent causes a reaction (a reduction) in which the product has more bonds from carbon to hydrogen (or fewer bonds to oxygen) OH O 4 R C 4 R C R' + 1 NaBH4 then H2O H R' MECHANISM NaBH4 transfers a hydride ion to the carbonyl carbon. The oxygen anion eventually removes a proton from water. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Synthesis) Weigh 9-fluorenone into 50 mL flask with stir bar. Dissolve in ethanol. Add NaBH4 slowly. Stir 20 minutes. Add deionized water. Add 0.1 M HCl dropwise until pH = 7. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Purification) Suction filter. RINSE SOLID WITH 10 ML COLD WATER! Prepare TLC and HPLC samples. Place product in warm oven for 10 minutes on a preweighed watch glass. Obtain final product yield, calculate % yield. Proceed to PRODUCT ANALYSIS. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE (Product Analysis) TLC analysis Identify components present in product solution and determine purity. HPLC analysis Identify components present in product solution and determine purity. MP analysis Compare to literature value of melting point to determine purity. NMR analysis Characterize reactant and product using spectra on page 169. Table 20.1 Determine whether 9fluorenone or sodium borohydride is the limiting reagent first. Remember stoichiometry! Theoretical yield (g) Actual yield (g) % yield Melting Range (oC) Product Appearance Record physical state and color of product. Table 20.2 calculate based on 9fluorenone and sodium borohydride ONLY! Review Experiment 13 for calculation! Atom Economy Experimental Atom Economy Eproduct Cost per gram Review Experiment 13 for calculation! Review Experiment 13 for calculation! Calculate COST PER SYNTHESIS 1st based on all reactants and solvent! Tables 20.3 and 20.4 Compound 9-fluorenone 9-fluorenol TLC Rf values Standards Sample Compound Rf values are unitless and 2 decimal places ONLY! 9-fluorenone 9-fluorenol HPLC Retention times (min) Standards Sample Area % NMR Spectroscopy 9-fluorenone O Aromatic protons 9 Aromatic carbons 194d NMR solvent NMR Spectroscopy 9-fluorenol Aromatic protons 5.54d TMS 1.75d Aromatic carbons NMR solvent 75d SAFETY CONCERNS All compounds used in today’s experiment are FLAMMABLE and TOXIC! Use extreme caution when in use! • WASTE MANAGEMENT Place aqueous filtrate from suction filtration in container labeled “AQUEOUS WASTE (Ketones)”. Place TLC solvent in container labeled “ORGANIC WASTE (Ketones)”. Place MgSO4, filter papers, and used TLC plates in yellow “SOLID WASTE” can. Place used TLC and melting point capillaries in BROKEN GLASS CONTAINER. Place product in container labeled “9-FLUORENOL (Student Prep). CLEANING Clean all glassware with soap, water, and a brush if necessary. Rinse all glassware with wash acetone before returning it to the lab drawer! DO NOT return glassware to lab drawer dirty or wet!