Experiment 21
advertisement

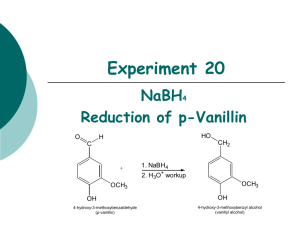
Experiment 20 NaBH4 Reduction of p-Vanillin O HO H CH2 C + 1. NaBH4 2. H3O+ workup OCH3 OCH3 OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (p-vanillin) OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl alcohol (vanillyl alcohol) Objectives: To synthesize vanillyl alcohol by reduction of p-vanillin using NaBH4. To purify the product by recrystallization. To identify product and analyze the purity using TLC, HPLC and melting point analysis. To characterize the reactants and product using 1H-NMR and IR spectroscopy. Before coming to lab… Review these techniques: Vacuum filtration Recrystallization TLC Analysis HPLC analysis Melting point analysis CHEMICAL EQUATION This is provided as a solution. Be sure you understand how to calculate theoretical yield! O HO H CH2 C + 1. NaBH4 2. H3O+ workup OCH3 OCH3 OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (p-vanillin) OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl alcohol (vanillyl alcohol) MECHANISM O H C O H H B H H C HO H CH2 H O H H H + H2O + B(OH)3 (from 6M HCl) OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (p-vanillin) OCH3 OCH3 OCH3 OH OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzyl alcohol (vanillyl alcohol) REDUCING AGENTS Reducing agents cause a reaction resulting in a product containing more bonds from carbon to hydrogen (or fewer bonds to oxygen). NaBH4 (sodium borohydride) is a versatile and useful reducing agent in organic chemistry, however will only reduce carbonyl groups of aldehydes and ketones. LAH (lithium aluminum hydride) is another common reducing agent, however use of this reducing agent will result in the reduction of many other carbonyl containing compounds, including esters, carboxylic acids H H Li+ Na+ and amides. H B H H Sodium borohydride H Al H H Lithium aluminum hydride H Hydride ion TLC STAIN—2,4-DNP R H C HN NH 2 HN O NO2 N NO2 + H R aldehyde or ketone NO2 2,4-DNP (red-orange) NO2 product hydrazone (yellow-orange) 2,4-DNP is a TLC stain used to detect aldehydes and ketones OVERVIEW Dissolve p-vanillin in ethanol. Add NaBH4 solution drop-wise via addition funnel while stirring. Add 6M HCl to hydrolyze intermediate, forming alcohol product. Isolate crude product by vacuum filtration. Recrystallize the product from ethanol. Prepare TLC and HPLC samples—submit HPLC sample for analysis. Perform TLC experiment on product, staining with 2,4-DNP stain. Obtain final mass of product and calculate % yield. Perform melting point analysis. Identify IR absorptions and 1H-NMR signals using provided spectra. Analyze HPLC results. SYNTHESIS Mix p-vanillin and ethanol in a water cooled 25 mL flask with stir bar until dissolved. Set up apparatus shown. Add NaBH4/NaOH solution to separatory funnel. Add a few ice cubes to the water bath. Begin adding NaBH4/NaOH solution SLOWLY. 7 8 6 5 4 3 2 9 1 0 1 7 8 9 6 5 11 4 3 2 1 SYNTHESIS Remove water bath. Stir 5 min. Return ice water bath. Add 6M HCl until pH = 6. Stir for 10 min. in ice bath. CRUDE PRODUCT ISOLATION Suction filter to isolate crude solid. Rinse solid in funnel with icecold water. Dry solid under vacuum for a few minutes. PURIFICATION— Recrystallization Transfer crude solid to a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask using a powder funnel. Rinse funnel with ethanol. Heat to dissolve product. Remove and filter to remove boric acid. Transfer filtrate to preweighed 150 mL beaker and evaporate solvent. Reweigh to obtain final product mass. Proceed to PRODUCT ANALYSIS. PRODUCT ANALYSIS Prepare TLC and HPLC sample of solid product. Submit HPLC sample for analysis. Prepare TLC plate using sample and provided standards. filter paper Develop plate and visualize under UV. A Stain plate with 2,4-DNP TLC stain. B C PRODUCT ANALYSIS—TLC TLC Analysis Used to identify and determine purity of products at the end of the experiment. 2,4-DNP will be used as a stain to detect the presence/absence of the aldehyde functional group. Table 20.1 TLC Results Rf values should always be recorded to 2 decimal places! Never more, never less! Compound p-vanillin Vanillyl Alcohol Standard Rf Sample Rf TLC Diagram Sketch the plate as much to scale as possible! Include cm measurements for all spots and solvent front! PRODUCT ANALYSIS—IR IR Analysis IR spectra of reactants and products can be used to determine the presence and absence of certain types of functional groups which indicate the conversion of one compound to another during the course of the synthesis. Table 20.2 IR Analysis Functional Group OH stretch C-O stretch C=O stretch Base Values p-vanillin Vanillyl alcohol Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) Frequency (cm-1) 3200-3600 1000-1300 1680-1740 Notice that the product should have 2 entries for O-H and C-O! PRODUCT ANALYSIS—NMR NMR Analysis 1H-NMR spectra of reactants and products can be used to determine the presence and absence of certain types of signals which indicate the conversion of one compound to another during the course of the synthesis. O This is where the major change is! H1 C 6 2 HO 7 CH2 1 6 2 5 5 OCH3 OCH3 3 3 OH 4 OH 4 Tables 20.4 and 20.5 O H C Table 20.4: Experimental Results CH2OH Theoretical yield (g) Actual yield (g) Percent yield Product Appearance Experimental Melting Point (oC) NaBH4 sodium borohydride $112.20/100g CH3CH2OH OCH3 OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy benzaldehyde (p-vanillin) $13.10/100g ethanol $23.66/500mL OCH3 OH 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy benzylalcohol (vanillyl alcohol) $22.90/50g Table 20.5: Green Chemistry Results Atom Economy (%) Experimental Atom Economy (%) “Eproduct” Cost per synthesis ($) Cost per gram ($/g) PRODUCT ANALYSIS—HPLC HPLC Analysis Used at the end of the experiment to identify and quantify compounds present during the synthesis, as well as the purity of the final products from each step. Table 20.6: HPLC Analysis Compound p-vanillin Vanillyl alcohol HPLC Retention Times (min) Standard Sample PRODUCT ANALYSIS—HPLC HPLC Analysis Used at the end of the experiment to identify and quantify compounds present during the synthesis, as well as the purity of the final products from each step. Compound p-vanillin Vanillyl alcohol HPLC Retention Times (min) Standard Sample SAFETY CONCERNS Ethanol, ethyl acetate, hexane, and acetone are all FLAMMABLE materials. Sodium borohydride and 2,4-DNP are TOXIC in large concentrations. Sulfuric acid, used to prepare 2,4-DNP stain, is CORROSIVE. WASTE MANAGEMENT o LIQUID WASTE : Place all liquid waste into this container including filtrates and aqueous washes from extraction. o GLASS WASTE: Place used TLC and melting point capillary tubes in this container. o PAPER WASTE: Place any gloves, TLC plates, filter papers, paper towels, etc. in the yellow trashcan. CLEANING Any glassware used to contain only volatile organic solvents can simply be rinsed with wash acetone. All other glassware should be cleaned with soap, water and brush, then rinsed with wash acetone or hand dried. IN LAB QUESTION (The following question should be answered in laboratory notebook.) Draw the product, and a complete mechanism for its formation, for the following reaction. In your mechanism, use only the hydride ion as your nucleophile. O 1. NaBH4 2. H3O+ workup ?