Phylum Porifera,Cnidaria & Platyhelminthes
advertisement

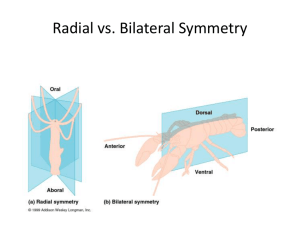
• Sponges have eukaryotic cells with cell membranes • They are a collection of cells organized into an organism with no tissues or symmetry • Sponges have cells lining the gastrovascular cavity that individually take in food by sifting particles from the water, so they are filter feeders • Substances are circulated via the water • Cells release waste by diffusion • No real response to environment • Do not move • Reproduction asexual by budding or gemmules • Sexual by releasing sperm into the water which fertilizes eggs inside the sponge • The simplest phylum of animals • Eukaryotic cells • radial symmetry • They are unique due to stinging cells (nematocysts) that paralyze prey • Circulation and excretion by diffusion through body wall • Respond to environment by some specialized sensory cells, nerve net, • Sea anemones can creep and burrow, some use water and gastrovascular cavity as a hydrostatic skeleton • Alternate between sexual (external fertilization) and asexual by budding • Groups: Hydra, corals, sea anemones, jellyfish • Ecological role: build reefs vital to coastal ecosystems which are some of the most productive on earth • Flatworms have eukaryotic cells • Flatworms are unique because they have no coelom (acoelomates) and have a one opening gastrovascular cavity • 3 germ layers • Circulation by diffusion, gas exchange (respiration) by diffusion • Excretion-some have flame cells that remove excess water and nitrogenous wastes • Response-ganglia (groups of nerve cells) connected by nerve cords with eyespots and specialized sensory cells • Movement by cilia and muscle cells in free-living forms • Two types of feeding-some are parasitic, feeding on predigested food by the host or blood • Free-living forms like the planarian suck food into pharynx and undigested waste out the same opening • Reproduction-free-living forms hermaphrodites and can reproduce sexually or asexually • Parasitic sexual or asexual by fission • Ecological role-parasites or free-living scavengers • Groups: Trematodes-parasitic flukes • Cestodes-Tapeworms • Turbellarians- planarians, free-living scavengers