Animal Biology Study Guide: Systems, Characteristics, Phyla
advertisement

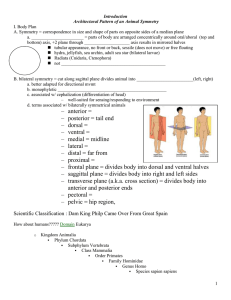
Terms to Study Body Systems What challenges are animals faced with as larger, multi-celled organisms? How do humans (an example of a higher order of mammals) overcome these challenges? What organs assist them with these processes? Animal Characteristics Concepts: Digestion types External and internal Stomach and Gastrovascular cavity Support Exoskeleton and endoskeleton types Advancement of tissues in animals Reproduction methods Budding Fragmentation Regeneration Parthenogenesis Asexual vs sexual Hermaphrodites Internal and external digestion Embryo development in animals Blastula, Gastrula Mesoderm, endoderm, ectoderm Aceolomate, Coelomate, Pseudocoelomate Protostome, Deuterostome Symmetry types Bilateral Radial Asymmetrical Cephalization Skills: Compare and contrast gastrovascular cavity function versus stomach function. Give examples of organisms that perform the various types of reproduction from above. Compare and contrast the development of protostomes and deuterostomes. Identify varying symmetry types in organisms. Questions: 1. 2. Why was the development of tissues in animals an important step in their evolutionary advancement? In what way does endoderm development determine complexity of the organism which is being developed? 3. Use the three Phylums of worms to explain the three types of coelome development. Sponges/Porifera Concepts: Structure Osculum Spicules Cellular structure Porocytes Choanocytes Ameobocytes Sponge symmetry Sponge reproductive cycle Asexual and sexual Sponge reading Sponges are the base of the tree of life based on DNA sequencing Sponges are more closely related to fungi than plants Sponge coelome development and its implications for tissue development Skills: Determine how the sponge structure allows it to do the following things: excrete waste, digest food, collect food, reproduce, support its body, circulate foods throughout its body. ID a sponge under a microscope based on spicules. Explain water flow through a sponge. Questions: 1. 2. 3. What is the difference between the three classes of sponges? What characteristics specifically make sponges the most primitive of animals? Why does poor water quality have a major effect on sponges? Cnidarians Concepts: Medusa Structure Bell Ring Canal Gastrovascular cavity Tentacles Oral arms Gonads Polyp structure Retractor muscle Gastrovascular cavity Gonads Cellular structure Cnidocytes Nematocysts Cnidarian symmetry Nerve net in cnidarians Cnidarian reproductive cycle Asexual and sexual Jellyfish reproduction as a focus (strobilus and ephyra development) Cnidarian coelome development and its implications for tissue development Hydrozoa Anthozoa Scyphozoa Man-o-war jellyfish Box jellyfish Bioluminescence importance in cnidarians Zooxanthellae Coral bleaching Obelia Skills: ID polyp and medusa stages of cnidarians and explain the similarities and differences. Explain the feeding responses and digestion in cnidarians. Explain the action of the cnidocyte. ID ancient cnidarian fossils and explain the appearance of Iowa when they lived. Compare and contrast hard and soft corals. Questions: 1. 2. 3. In what way can the ring canal be considered a circulatory system? What is coral bleaching and what factors are leading to it? In what ways are cnidarians more advanced than sponges?