Kingdom Animalia
advertisement

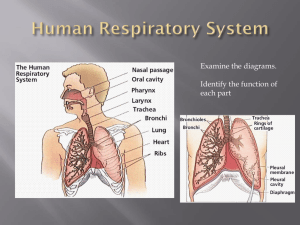
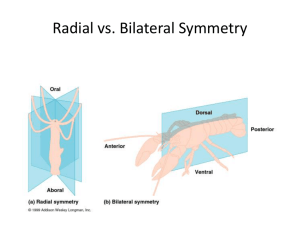
Kingdom Animalia Characteristics no cell walls sexual reproduction is common most are mobile multicellular, heterotrophic Specialized tissue develop in the embryo during GASTRULATION A fertilized egg divides and becomes a BLASTULA (hollow ball of cells) which then pinches inward to form a GASTRULA which has the 3 germ layers Endoderm - becomes the lining of the gut Ectoderm - becomes the skin and outer layer, including nervous tissue Mesoderm - the middle layer, the muscles and bones The common ancestor of animals is thought to be the CHOANOFLAGELLATES, from which all major animal groups branch from Definitions Parazoa - sponges, organisms with no true tissues (cells within sponges are called Choanocytes, which absorb nutrients) Eumetazoa - all other animals with true tissues Radiata - animals with radial symmetry (hydra, jellyfish) Bilateria - animals with bilateral symmetry ( dogs, worms, humans). They have a top (dorsal) and a bottom (ventral), front end (anterior) and behind (posterior) Acoelomates - have no blood vascular system, and lack a cavity between the gut and outer body wall (flatworms) Pseudocoelomates - animals that have a fluid filled body cavity, but not enclosed by mesoderm Coelomates - have a true coelom (body cavity) Protostomes - first embryonic indentation becomes the mouth Ex. annalids, arthropods, mollusks Deuterostomes - the first indentation develops into the anus Ex. chordates and echinoderms (starfish) Major Animal Taxa 1. Porifera - sponges 2. Cnidaria - jellyfish, hydra. They lack a mesoderm and are radially symmetrical 3. Platyhelminthes - flatworms (flukes, planarians, tapeworms), cephalization (to have a head end) 4. Rotifera - tiny worm like creatures, with a complete digestive tract 5. Nematoda - roundworms 6. Molluska - clams, squid, snails, slugs. 7. Annalids - segmented worms, earthworms and leeches 8. Arthropods - have hard exoskeletons made of chitin. Lobsters, crabs, insects, isopods 9. Echinodermata - starfish 10. Chordata - includes a couple of nonvertebrates (lancelets and sea squirts) and then all the vertebrates There are four features common to chordates dorsal nerve cord - forms the nervous system and becomes the brain and spinal cord in vertebrates notochord - long support rod that is replace by bone in most Pharyngeal slits - slits in the pharynx area that become respiratory structures (gills) Tail - extension past the anus, though it is lost in most