Exam I Study Guide
advertisement

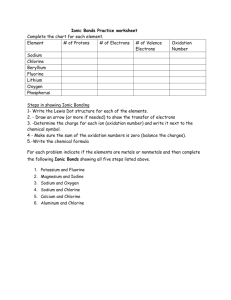
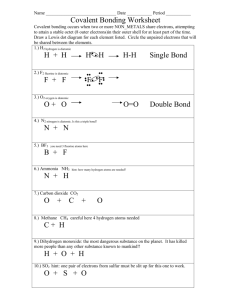
Biology 110 Bio 110 Exam I Study Guide Chapter 1 1. Define the following: a. Abdominal cavity b. Abdominopelvic cavity c. Anatomy d. Cranial cavity e. Disease f. Distal g. Frontal plane h. Homeostasis i. Lateral j. Lumbar k. Medial l. Mediastinum m. Negative feedback n. Organ transplantation o. Pelvic cavity p. Pericardial cavity q. Physiology r. Pleural cavity s. Proximal t. Sagittal plane u. Spinal cavity v. Systemic disease w. Thoracic cavity x. Transverse plane y. Visceral 2. How is the structure of an organ related to its function? Give an example. 3. What are the levels of structural organization of the body? 4. What is a tissue? 5. How many tissues make up an organ? 6. What is an organ system? 7. What is the standard anatomical position? 8. Know all the planes and what you get when you slice a body up through each one 9. Know all those directional terms (relative positions of body parts). 10. What do you find in the axial portion of the body? 11. What do you find in the appendicular portion of the body? 12. List the cavities of the body and what they contain. 13. What smaller cavities are found in each? 14. What are the 9 anatomically defined abdominopelvic regions? 15. …and those quadrants? 16. What is homeostasis? 17. How is it maintained (homeostasis)? 18. How do negative and positive feedback mechanisms work? Biology 110 Chapter 2 1. What is a proton? What is its charge? What is its mass? Where is it found? 2. What is a neutron? What is its charge? What is its mass? Where is it found? 3. What is an electron? What is its charge? What is its mass? Where is it found? 4. What is the definition of atomic number? 5. In an element the number of electrons is equal to the number of what other subatomic particle? 6. What is the atomic mass of an atom equal to? 7. What is an isotope? 8. What is an ion? 9. How is an ion formed? 10. Why is an ion formed? 11. What is the rule of eights? 12. When ions are formed are electrons donated, accepted, or shared? 13. How are covalent bonds formed? 14. Are the electrons that form a covalent bond shared equally? 15. What is the difference between a polar and nonpolar covalent bond? 16. What is a hydrogen bond? 17. Which type of bond is the strongest? Which type is the weakest? 18. Fluorine has the atomic number 9, sodium has the atomic number 11. a. What is the number of protons in each element? b. The atomic mass of fluorine is 19 and sodium 23. What would you guess the number of neutrons to be in each element? c. How many electrons would each element have? 19. Knowing that having 8 electrons in the outer shell will make the element more stable, which of the following correctly describes the way fluorine and sodium will form a bond: a. Fluorine will donate a proton to sodium b. Sodium will donate a proton to fluorine c. Fluorine will donate a neutron to sodium d. Sodium will donate a neutron to fluorine e. They will share 8 electrons to form a covalent bond f. Sodium will donate an electron to fluorine, and become an ion g. Sodium will accept an electron from fluorine, and become an ion h. Fluorine will donate an electron to sodium, and become an ion i. Fluorine will accept an electron from sodium, and become an ion j. The ions will be attracted because of their charge difference and form an ionic bond k. When chlorine accepts an electron to become an ion what charge does the chlorine ion have and why? 20. What is the difference between an element and a molecule and a compound? 21. Can an element have different kinds of atoms (don’t count isotopes)? 22. How about a molecule? 23. Does a compound have different kinds of molecules? 24. Can a compound have different kinds of atoms? 25. Will an ionic bond break easily in water? Will a covalent bond do the same thing? 26. Why is water a polar molecule? 27. What properties does the molecular structure of water allow it to have? 28. What is cohesion? What does it allow water to do? 29. Why is a high heat of vaporization good? 30. Why is water a good solvent? 31. What does a non-polar compound do in water? 32. Does water dissociate? Into what? Biology 110 33. What is a condensation synthesis (dehydration) reaction? 34. What is a hydrolysis reaction? 35. What is an electrolyte? 36. What is the difference between an acid and a base? 37. How is acidity measured? 38. Would a solution with a pH of 6.5 be acidic, basic, or neutral? 39. What is the pH of a neutral solution? 40. What is acidosis? 41. What is alkalosis? 42. What is a buffer? 43. Identify which of the following are lipids, which are carbohydrates, which are proteins, and which are nucleic acids: a. Fatty acids b. Glycogen c. Triglycerides d. Cholesterol e. Phospholipids f. Glucose g. Sucrose h. Monosaccharides i. Polysaccharides j. Glycerol k. DNA l. RNA m. Enzymes n. Chains of amino acids 44. Which of the following contains nitrogen: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids 45. What are the functions of carbohydrates? 46. What are the building blocks of carbohydrates? 47. What is a polysaccharide? 48. What are the functions of lipids? 49. What are the components of triglycerides? 50. What are steroids? 51. What are phospholipids? What does the phosphate group do for the lipid? 52. What are the functions of proteins? 53. What are the building blocks of proteins? 54. What kind of bond links the subunits of proteins? 55. What is the difference between a structural and functional protein? 56. What are the four levels of protein structure? 57. What are enzymes? 58. What is denaturation? What kinds of things cause it? 59. What are the 3 basic building blocks of a nucleotide? 60. What are the rules for hydrogen bonding between nitrogenous bases? 61. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? Yes, of course I mean both structurally and functionally. 62. Which nucleotides are found in DNA? How about RNA? 63. What is a gene? 64. If a section of a DNA strand has the bases ATTGACT what bases will the opposite strand have? 65. What is special about ATP? (What does it do?) Biology 110 Chapter 3 1. What are the structural components of the plasma membrane? 2. What is a phospholipid bilayer? 3. What does cholesterol do for the plasma membrane? 4. What is the function of proteins in the plasma membrane? 5. What is the role of sugar residues on the plasma membrane? 6. What are the major components of the nucleus? 7. What is the difference between chromatin and chromosomes? 8. What is the function of messenger RNA? 9. What is a mutation? 10. What is the function of the nucleolus? 11. What is the cytoplasm primarily composed of? 12. What is the function of a ribosome? 13. What is transfer RNA? 14. What is ribosomal RNA? 15. What is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? 16. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER? 17. What are peroxisomes? 18. What is the Golgi apparatus 19. What are lysosomes? 20. What are mitochondria? 21. What are centrioles? 22. What is the difference between cilia and flagella? 23. What is the difference between active and passive transport? 24. Define diffusion, osmosis, and filtration. 25. Where does the energy for active transport come from? 26. What is endocytosis? 27. What is the difference between pinocytosis and phagocytosis? 28. What is exocytosis? 29. Describe DNA replication. 30. Describe protein synthesis. 31. What are the two types of cell division and what is the difference between them? Biology 110 Chapter 4 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What are the four major types of tissues? What functions may epithelial tissues perform? How are epithelial tissues classified (shape and layers)? What is function of connective tissue? Which types of connective tissue have the following types of cells: fibroblasts, adipocytes, chondroblasts, chondrocytes, osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts, hemocytoblasts (hematopoietic stem cells)? 6. What are the components of connective tissue? (cells and matrix, matrix may have fibers) 7. What is the difference between loose and dense fibrous connective tissue? 8. What is cartilage? How is it classified? 9. What is special about the matrix of bone? 10. What is special about the matrix of blood? 11. What is muscular tissue composed of? 12. What are the major filaments in muscle? 13. What are the 3 types of muscle and where are they found? 14. Which has the following characteristics: striations, is voluntary, is involuntary, has intercalated disks. 15. What are intercalated disks? What 2 types of junctions do they have? 16. What is nervous tissue? 17. What types of cells are found in nervous tissue? 18. What are 3 types of cell junctions? What is the function of each? 19. What type of tissue are glands composed of? 20. What is the difference between exocrine glands and endocrine glands? 21. Is a goblet cell a unicellular gland? What do goblet cells secrete? 22. What are the different types of membranes? 23. What organs or structures is each type of membrane associated with? 24. What are the functions of each type of membrane?