Handout
advertisement

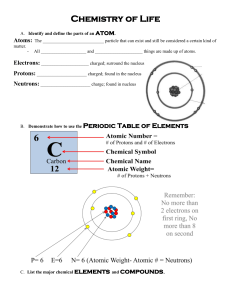
Chemical Bonding A chemical bond is the attraction between atoms that results in the formation of a molecule. 1. Sometimes molecules are called compounds. Learn more: http://education.jlab.org/qa/compound.html 2. Apply what you just learned - label the following as molecules and/or compounds. Explain why you labeled each the way you did. Cl2 MgCl2 3. All molecules are compounds. Agree or disagree with this statement and explain why. Use this resource to answer the following questions. http://www.visionlearning.com/library/module_viewer.php?print=1&mid=55&mcid 4. Compare a compound to its component elements. Give an example to illustrate the difference. 5. In 1916, Gilbert Newton Lewis explained why bonds formed. What would be his answer to this question: Why do atoms form bonds? 6. Differentiate between ionic and covalent bonds. Include three differences. Be sure to watch the animations. 7. Differentiate between polar and nonpolar covalent bonds. 8. When a molecule has a difference in electrical charge (a positive pole and a negative pole), what’s it called? Watch the online tutorial and answer the questions. www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/animations/chang_7e_esp/bom1s2_11.swf 9. Write the Lewis Dot Structures for sodium (Na) and fluorine. Show how they bond to achieve a stable octet. What type of bond do they make? 10. What is an ion? When do ions form? 11. What type of ion is sodium (Na)? 12. What type of ion is fluorine (F)? 13. Write the Lewis Dot Structures for the two fluorine atoms. Show how they bond to achieve a stable octet. What type of bond do they make? 14. In a nonpolar bond between two atoms, are the electrons shared evenly or unevenly? 15. Write the Lewis Dot Structures for the fluorine and hydrogen atoms. Show how they bond to achieve a stable octet. What type of bond do they make? 16. In a polar bond between two atoms, are the electrons shared evenly or unevenly? 17. What can you infer about the electron affinity of the fluorine atom as compared to the hydrogen atom?