Math 4030 Final Exam Review
advertisement

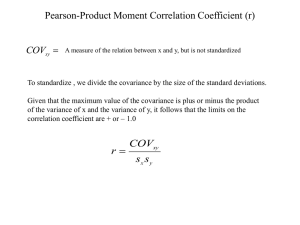
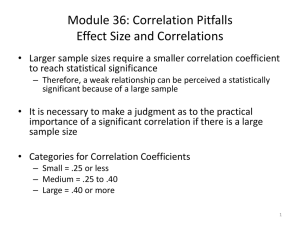
Math 4030 Final Exam Review Probability (Continuous) • • • • Definition of pdf (axioms, finding k) Cdf and probability (integration) Mean and variance (short-cut formula) Properties of Mean and variance (linearity, independent, …) • Continuous distribution: Uniform, Normal, Gamma (Exp, Chi-square as special cases), Beta, Weibull. (Mean, variance, tables, integral for simple values of parameters) • Use of Tables: normal, t, chi-square, F. • Two RV’s: joint, marginal, conditional, independency, mean and variance, covariance. (Double integration.) (Are X and Y independent?) All about Normal: • Properties of normal distribution: parameters, standard normal, mean and variances, linear combinations; • Find probabilities; • Find the cut-off scores, z notation; • Normal approximate binomial, correction for continuity. Sample Statistics and Their Distributions: • Sample means distribution (t or z?) • Central Limit Theorem and application • Sample variance and standard deviation (Chi-square or F?) • Sample proportion: binomial and normal • Sample size calculation. Confidence intervals: • Concepts: point estimation, maximum error, and confidence level; • C.I. for population mean ; • C. I. for difference of two means; • C.I. for population variance or standard deviation; • C.I. for population proportion; • C. I. for difference of two proportions; • C.I. for parameters in linear regression; • C.I. for correlation coefficient. Hypothesis Testing: • Concepts: Null vs. Alternative hypotheses, tails, critical value(s), critical region, P-value, types of errors, conclusion. • Hypothesis testing regarding • Mean from one sample (z or t); • Mean from two samples (dependent or independent? Equal or unequal variances? Z or t?); • Proportion from one sample; • Proportion from several samples (r by c table); • Goodness of Fit Test; • Slope and intercept in the linear regression; • Correlation coefficient. General Procedure: 1. Null and alternative hypotheses (what is the claim?) (1 point) 2. Level of significance (left-tail, right-tail, or two-tail test) (1 point) 3. Decide the distribution to use and find the critical value(s) or region. Calculate the corresponding z-score, t-score, chi-square score, or F-score, from the sample statistics. (2 points) 4. Conclusion (1 point) • Reject or not reject the null hypothesis • Make comment about the claim. Linear regression: • Concepts: identify the linear correlation from scatter plots; • Calculate correlation coefficient: strength vs. significance. • Find Linear regression line: method of the least squares • Prediction and errors; • Meaning of correlation coefficient, slope of the regression line, and coefficient of determination (r-squared) What to bring and what not to bring: Allowed: • Non-programmable calculator; • 2 page (4-side) letter size formula sheet. Not allowed: • Textbook and any notes beyond 2 page limit; • Calculator that are built in any other electronic device (tablets, cellphone, etc.) No need to bring: • z-table, t-table, chi-square table, and F-tables. Need extra help? Office Hours (RB 2007): Thursday Dec. 3: 9:00 – 11:00 AM Tuesday Dec. 8: 9:00 – 11:00 AM Friday Dec. 11: 9:00 – 11:00 AM LUMAC (Li 2004)