unit i central prolems of an economy
advertisement

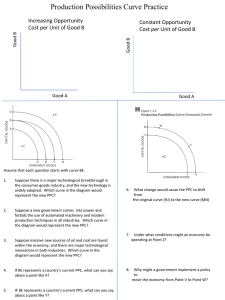
UNIT I CENTRAL PROLEMS OF AN ECONOMY I Central Problems of an economy (i) Problem of allocation What to Produce – It is a problem of selection of good and its quantity to be produced. As resources are limited , the producer has to make this choice . He can produce Consumer goods / Capital goods , Necessary goods / Luxury goods etc How to Produce – It is a problem of choice of technique of production . Producer may use Labour-intensive or Capital Intensive technique. To minimise his cost of production , the producer has to select the technique. For whom to Produce – It is a problem of distribution of National Output or income among the people in the economy. (ii) Problem of Full and efficient use of resources (iii) Problem of Growth of resources II Why do the Central problems arise ? (i) Unlimited human wants having different priorities (ii) Limited resources with alternative uses Hence , Central problem arises due to SCARCITY of resources. III Production Possibility Curve ( PPC) / Transformation Curve Meaning -- A curve showing different possibilities of production of two goods with full use of given resources and technology . Nature of PPC – (i)PPC is a downward sloping curve As resources are fully employed, the producer can increase production of one good by reducing production of the other. So PPC is downward sloping. (ii)PPC is concave to the origin PPC is concave because of increasing marginal opportunity cost ( increasing MRT) . As resources are use specific , the producer has to give up more and more unit of one good to get every additional unit of a good. Note : (i) PPC is Concave when MOC or MRT is increasing (ii)PPC is Convex when MOC or MRT is decreasing (iii)PPC is straight line when MOC or MRT is constant PPC IS CONCAVE TO THE ORIGIN IN REAL LIFE BECAUSE RESOURCES ARE USE-SPECIFIC AND MOC or MRT is increasing. IV Central Problems with PPC Point on PPC shows full employment of resources Point inside PPC shows under-utilization / inefficient use of resources -- If resources are better utilised / efficiently utilised , the economy will move from from a point inside PPC to a point on PPC. Example – Unemployment of labour in India, Under-utilisation of existing capital in India etc Swachha Bharat Abhiyan scheme, Employment generation scheme etc of the govt helps Indian economy to move a point inside PPC to a point on PPC. Rightward shift of PPC shows Growth of Resources -- PPC of an economy will shift rightward if there is growth of resources in the economy. Example – Foreign investment in the country, Migration of labour from abroad to India, Supply of skilled labour in India, Introduction of all Education expansion scheme by the govt, Make In India scheme to increase inflow of foreign capital in India , Immunization for all children by 2020 scheme of govt (Mission Indradhanus scheme) , exploration of new resource (new oil field etc) in the country, advancement in technology in India etc. Leftward shift in PPC shows destruction of resources / decrease in resources -- If there is destruction / decrease of resources in India , PPC will of India will shift leftward. Example – Destruction of resource due to natural calamities (flood/ draught/ fire etc) in India , Migration of labour from India to abroad, Large scale Outflow of capital from India etc. V Marginal Opportunity Cost (MOC) / Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT) MOC shows the amount the good the producer has to give up to produce an additional unit of a good. MOC = Loss of good / Gain of good Example : Production Possibilities A B C D E Good X Good Y 0 5 10 15 20 100 90 70 40 0 MOC or MRT = Loss / Gain -10/5 = 2 20/5 = 4 30/5 = 6 40/5 = 8 Remarks MOC or MRT is increasing . Hence PPC is concave . Diagram -Good Y Y1 Y2 X1 X2 Good X MOC = Loss / Gain = Y1Y2 / X1X2 VI Opportunity Cost It is the value of a factor in its next best alternative foregone . Opportunity cost is the opportunity lost. Example : A plot of land can be used for rice production ( Rs 200) or wheat production (Rs 100) or pulses production (Rs 150). If the producer produces rice then he has to give up production of wheat and pulses. Opportunity cost of Rs 200 rice production is Rs 150 pulses production. In previous diagram , Opportunity cost of (X1X2) unit of good X is (Y1Y2 ) unit of good Y. VII Micro Economics The branch of economics which deals the economic problems of an individual firm or consumer . Eg. Profit of a TV company is increasing , Consumer equilibrium etc. VIII Macro Economics The branch of economics which deals with economic problems at the level of an economy as a whole. Eg. Problem of unemployment in an economy.