honorseconstudy1-2 - Honors Government & Economics
advertisement

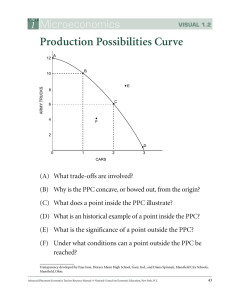
Honors Economics Chapters 1 & 2 Study Guide Chapter One: Trade-off: Opportunity Cost: Marginal Benefit: Consumer Goods: Capital Goods: Economics: Consumers: Economize: Positive Economics: Normative Economics: Services: Producers: 1) An economist’s tool useful for showing changes over time would be a __________ graph. __________ graphs are useful for comparing items for a single measure. _______ graphs show how parts make up a whole. 2) A ______________ __________________ ____________ shows all of the possible combinations of 2 goods or services that can be produced through the use of available resources. Another name for the PPC would be the Prod. Possibilities ___________. (PPF) Using a PPC could help to increase a company’s ___________________. 3) The study of “Big picture” issues or issues that affect the entire nation’s economy would fall under ________________________. 4) When we make decisions in an attempt to maximize our utility we are acting out of ______ - ______________. According to Adam Smith this is what drives the economy forward through the “________________ _________.” 5) ________________ involves using resources to produce the maximum amount of goods and services. 6) A point on a PPC indicates that there is _____________ production because all resources are being used fully and __________________. A point inside the PPC indicates an ___________________ of resources, when a point outside the PPC indicates an ___________________ level of production during the time considered. 7) The economic problem deals with the fact that we must use limited ______________ to satisfy unlimited __________, which are ever changing. This forces people to make decisions about how to use _______________ effectively. 8) The implementation of new _________________ can often lead to increased efficiency. 9) An _________________ is a benefit that causes us to act a certain way. Know how to determine the opportunity cost of producing one good instead of another by looking at a PPC. This will always be measured in units of the _________ good. Be able to list and give an example for each of the 4 Factors of Production: You will have to think of a good/ service and identify an example of each factor involved. What is meant by the economic saying, “There is no such thing as a free lunch?” How specialization leads to greater productivity: Identify the 3 basic economic questions that all societies are forced to answer: Chapter 2 Traditional Economy: Command Economy: Market Economy: 1) The purpose of ____________ is to serve as a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a measure of value. 2) Mixed economies that are closest to the pure market model are classified as __________________. 3) Mixed economies that are closest to the pure command model are classified as __________________. (aka Authoritarian Socialism) 4) The feature that distinguishes the U.S. economy from the pure market model is limited ______________ _____________________. 5) The economic rivalry that exists between businesses that sell the same or similar products is called ___________________. This is beneficial to consumers by keeping prices __________ and improving the ____________ of goods and services. Identify the four types of economic systems discussed in class: - What 2 markets are exhibited in the circular flow model? All economies today can be classified as ___________ economies. Be able to discuss why the U.S. is considered to be this type of economy. Give specific examples of elements taken from traditional, command, and market systems. Indicate how 3 basic econ. Questions are answered in each system: Traditional: Command: Market: What causes the standard of living to rise or fall within a nation?: (Relationship between population growth and the average production of each worker) Identify the 5 features of a Market Economy: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5)