Scarcity: unlimited wants limited resources Increasing opportunity

Scarcity: unlimited wants limited resources
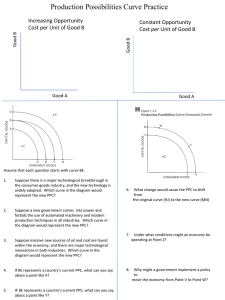
Increasing opportunity cost: as you increase what you produce, the opportunity cost also increases
What is the PPC (production possibilities curve) a model that shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scarce resources this model graphically demonstrates scarcity, trade-o ff s, opportunity costs, and e ffi ciency
-4 key assumptions: only two goods can be produced full employment of resources fixed resources (Ceteris Paribus) fixed technology anything to the left of the curve involves ine ffi ciency or unemployment anything to the right of the curve is impossible or unattainable given current resources
PPC demonstrates scarcity, trade-o ff s, opportunity costs, and e ffi ciency
-Production Possibilities Table each point represents a specific combination of goods that can be produced given full employment of resources
*Constant opportunity cost: resources are easily adaptable for producing either curve result is a straight line PPC (not common)
Increased opportunity cost results in a bowed out (convex) PPC
Decreased opportunity cost results in an inward (concave) PPC
Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost as you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost will increase
Why? resources are NOT easily adaptable to producing both goods
2 types of e ffi ciency:
-productive e ffi ciency- products are being produced in the least costly way; Any point on the curve
-allocative e ffi ciency- the products being produced are the ones most desired by society; the optimal point on this PPC depends on the desires of society
Shifting of PPC
3 shifters of a PPC change in resource quantity or quality change in technology change in trade increase in population: more production bc more workers shift outward (to the right) of the whole curve increased demand for product
Capital goods and Future Growth
-countries that produce more capital goods will have more growth in the future