MECH 351 - Concordia University
advertisement

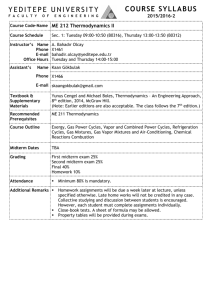
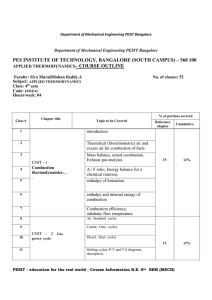
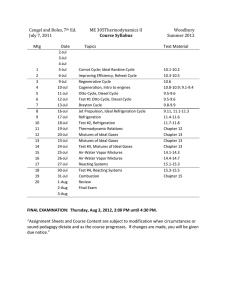
MECH 351 Winter 2015 CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS II (MECH 351), WINTER 2015, SECTIONS TX Instructor: Lectures: Section T and X Dr. Lyes Kadem, Room EV 4.207, Tel.: 514 848-2424 ext. 3143, Fax: 848-3175 E-mail: kadem@encs.concordia.ca website: users.encs.concordia.ca/~kadem Office hours: Tuesdays, Thursdays (11:00 am – 12:00 pm) Tuesdays and Thursdays, 13:15 – 14:30 SGW, in H – 937 Tutorials: TA TB TC TD MB-2.435 H-507 MB-2.445 H-539 Fridays, 14:45- 15:35 Mondays, 14:15-15:05 Fridays, 16:15-17:05 Mondays, 14:15-15:05 Objectives: This course applies the fundamental principles of thermodynamics presented in ENGR 251 to areas of particular interest to mechanical engineers. Topics covered are advanced cycles, real gases, non-reacting gaseous mixtures, and related theory. Prerequisites of this course are COMP 212 & ENGR 251. Textbook: “Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach” by Cengel and Boles, Any edition with SI units, McGraw Hill. Recommended References 1- "Fundamentals of Thermodynamics" by Sonntag, Borgnakke, and Van Wylen, 5 th edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1998. 2- “Thermodynamics” by K. Wark, 6th edition, McGraw Hill, 1999. 3- “Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics”, Moran, M.J. and Shapiro, H.N., 3rd ed., Wiley, 1995. 1/3 MECH 351 Winter 2015 Graduate attributes assessment: GRADUATE ATTRIBUTE A knowledgebase for engineering (A.1) Problem analysis (A.2) Design (A.4) INDICATOR EVALUATION TYPE OF EVALUATION Summative Target 1. Show competence in solving engineering or computer science problems 4. Overcome the limitations of theoretical modelling 1. Problem identification and formulation 2. Modelling 4. Analysis Midterm Q.1 Problem in Tutorial (Week 3) Formative 90% Final exam Q.1-5 Summative 70% (scale 0: none to 5: all) Midterm Q.1 Final Q.1 Summative Summative 70% 70% 2. Idea generation and selection 3. Detailed design 4. Validation and implementation Steam car project Formative 70% Steam car project Steam car project Formative Summative 70% 50% (binary scale) 70% Practice Evaluation: Course project Laboratory Midterm exam Final exam (closed book and notes) 10% (Energy management) 25% (15% for steam car project) 15% (Tentatively Feb 19, 2015) 50% However you must pass the final examination with a 50% grade to pass the course. ALL exams are mandatory and ALL exams will be counted. If you miss the midterm, it will be replaced by an oral theoretical examination (not necessarily covering the same topics as the regular midterm) Main Topics: Introduction and brief review of Thermodynamics I Vapor and combined power cycles (Chapter 10) Gas power cycles (Chapter 9) Refrigeration cycles (Chapter 11) Thermodynamic property relations (Chapters 12&13) Gas-vapor mixtures and air conditioning (Chapter 14) Chemical reactions and phase equilibrium (Chapter 15) 2/3 MECH 351 Winter 2015 Lecture notes, Assignments, Labs and General notes: Lecture notes will be available on the course website. Problem solving is an essential part of this course; you are encouraged to discuss the general principles involved in the homework sets with one another. The laboratories will start on Monday, January 12th. The lab manual describing all experiments and providing instructions concerning each experiment should be purchased from the bookstore. To take full benefit from the Lab., the students are urged to study carefully each experiment before performing it in the lab. The students have to get the lab. instructor's signature on their data sheet. Disclaimer: "In the event of extraordinary circumstances beyond the University's control, the content and/or evaluation scheme in this course is subject to change". No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thermodynamics II Assignments Topics Problem nos. (From 6th edition) 9.38, 9.56, 9.84, 9.88, 10.16 Review on ENGR251 10.C, 10.18, 10.19 Ideal Rankine Cycle Reheat Rankine Cycle, Regenerative Rankine 10.35, 10.49, 10.70 Cycle and Cogeneration 9.25C to 9.32C, 9.35, 9.37 Otto Cycle 9.54, 9.55, 9.57, 9.72, 9.93, 9.170 Diesel, Dual, and Brayton Cycles 11.4C, 11.5C, 11.14, 11.17 Refrigeration Cycles 13.1C to 13.8C, 13.12, 13.16C, Gas mixtures 13.17C, 13.30, 13.45, 13.55, 13.73 14.1C to 14.5C,14.18, 14.21C to Gas-Vapor Mixtures 14.24C, 14.32, 14.36C, 14.40, 14.69, 14.72, 14.76, 14.80, 14.95 15.19, 15.25, 15.32, 15.34, 15.66, Chemical Reactions 15.76. 15.89 Thermodynamics II Tutorials (From 6th edition) Topics Problem nos. 2.49, 4.9, 4.41, 4-70 Review on ENGR251 10-16, 10-20 Ideal Rankine Cycle Reheat Rankine Cycle, Regenerative Rankine 10-35, 10.49 Cycle and Cogeneration 9.35, 9.39 Otto Cycle 9.54, 9.93 Diesel, Dual and Brayton Cycles 11.11, 11.17, 11.23 Refrigeration Cycles 13.55, 13.71, 13.73 Gas mixtures 14.40, 14.69, 14.91 Gas-Vapor Mixtures 15.58, 15.70, 15.79 Chemical Reactions 3/3