Course Outline
advertisement

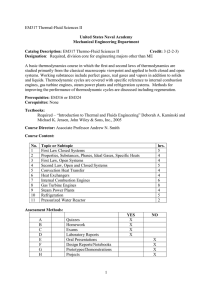
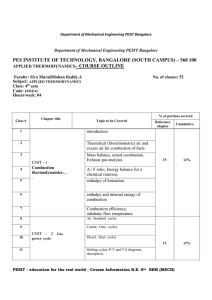
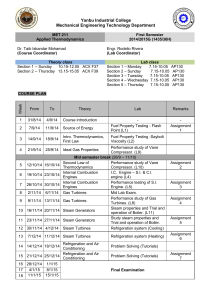
FREDERICK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Mechanical Engineering Programme of Study (Diploma/ 2 Years/System of Credits) Subject: Academic Year: Instructor: Number of periods per week: Number of total weeks: Thermodynamics II– AMEE 218 2004 - 2005 (Spring semester) Assistant Professor: Dr. Ashraf Bassily 3 14 Aim: Following the course AMEE 114, the emphasis of this course would be to provide a detailed presentation of the different thermodynamic cycles (heat engine cycles, steam cycles, refrigeration and internal combustion engines) and the equipment/processes involved. Hence, the students would get more experience in dealing with processes that occur in such equipment as a steam power plant, vaporcompression refrigerator, a thermoelectric cooler, a fuel cell and an internal combustion engine. Teaching Methods: Lectures, tutorials and laboratories are used in this subject. The evaluation is based on assignments/lab-reports, tests, mid-term and final exam. Site visits are also conducted in the content of this subject. Laboratories would run concurrently and the experiments would give students a better understanding of the theory learned and bring them in contact with the relevant equipment. In addition it will introduce the students to experimental measurements and a number of instruments. Emphasis would be given in preparing the laboratory reports and ways to present their data. Students should know the limitations of the instruments they use and be able to make comparisons between experimental and theoretical results. Course Outline Review of the first law of thermodynamics and thermodynamic properties. The Heat Engine Cycle: the Carnot cycle, the Carnot cycle for a perfect gas, the constant pressure cycle, the air standard cycle, The Otto cycle, The diesel cycle, The dual combustion cycle, mean effective pressure. Steam Cycles: the Rankine cycle, the Rankine cycle with superheat, the enthalpy – entropy chart, the reheat cycle, the regenerative cycle. Refrigeration: reversed Carnot cycle, vapor compression systems, refrigerating load. Introduction to IC and CI engines: four-stroke cycle, two-stroke cycle, criteria of performance. Introduction to chemical reactions: ideal mixtures, fuels, reactants, combustion, air-fuel ratio, enthalpy of formation. Laboratory Work: A selection of the following labs Experiment 1: Adiabatic Gas Law Experiment 2: Determination of the Specific Heat Capacity of a Liquid by the Method of Cooling. Experiment 3: Heat Efficiency and Temperature Difference Experiment 4: Thermocouple Response Characteristics Experiment 5: Refrigeration Experiment 6: Air-conditioning unit Experiment 7: Thermal Conductivity Experiment 8: Fuel Cell Notes: Regarding the experiments; handouts are given and explained prior to the experiment. The grade of a student is based on his/her performance during the laboratory exercise and on his/her lab report. The lab-report must be carefully prepared, explain the student’s work, include all the measurements, calculations and the appropriate error analysis, and give answers to the questions asked during the lab. Prerequisites: AMEE 114 Place of teaching: In an ordinary classroom and in the Mechanical Engineering lab. Relationship of subject to Course objectives: The content of this subject strongly addresses the course objectives. In particular, it reinforces the ability to comprehend fundamental scientific principles and engineering laws and develop analytical skills in order to formulate and solve engineering problems. In addition, it provides a general academic background in order to adapt to technological advancement in the context of Mechanical Engineering and lays the foundations for further education. Furthermore, laboratory work offers practical experience in the use of modern engineering instruments and reinforces understanding through computerized and other experimentation. Assessment: Final exam Coursework 60% 40% The passing mark is 50%. To pass the course you must get a 35% grade in both the coursework and the final exam. Coursework Contents Test 1: Test 2: Engines and steam cycles (first week of April) Refrigeration, internal combustion engines, and chemical reactions (second week of May) Note: The dates of the tests and assignments are likely to change slightly. Textbooks: Advanced Thermodynamics Engineering. Kalyan Annamalai, Ishwar Kanwar Puri, CRC Press, 2001. Applied Thermodynamics for Engineering Technologists. T.D. Eastop and A. McConkey, Longman 1997. References: Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics. Adrian Bejan, Wiley-Interscience, 2nd edition, 1997. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles, McGraw Hill College Div., 4th edition, 2001. Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics. M. Moran and H. Shapiro Wiley & Sons, 4th Edition, 2000.