Overview of Injury Research
advertisement

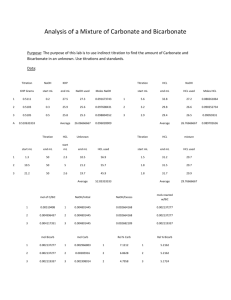
Buffering Capabilities of Guinea Pig Blood GROUP MB3 Kim Coughlan, Barry Huang, Laura Michelis, Le Truong Department of Bioengineering Background: Standardization of HCl with Na2CO3 12.000 10.000 8.000 pH Based on acid-base titration lab: wanted to further investigate significance of biological buffers • Determined buffer capacity of H3PO4 • HCO3- is primary biological buffer in blood Trial 1 Trial 2 6.000 4.000 2.000 0.000 0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 Above: Experimental titration curve of H2CO3 Hypothesis & Aims: This lab aims to examine how well pure bicarbonate buffer serves as a model for the buffering capabilities of real blood. Specifically, it is hypothesized that the buffering capacities of guinea pig blood and pure bicarbonate (at a similar concentration as that found in blood) will be the same. Department of Bioengineering 0.03 HCl added (mol) Methods & Protocol: • Calibrate the pH meter by following the instructions on the screen and by using the pH 4, 7, and 10 standard solutions. • Dilute 100mL samples of 25mM HCl and 25mM Na2CO3 • Titrate a 10mL sample of 25mM Na2CO3 with HCl, recording the pH every 0.5mL until the pH falls below 2. • Repeat above titration two times. • Titrate a 10mL sample of guinea pig blood with HCl, recording the pH every 0.5mL until the pH falls below 2. • Repeat above titration two times. • Create titration curves for all titrations and determine all pKa’s and buffer capacities. • Compare the buffer capacities of the Na2CO3 and guinea pig blood using a two-tailed two sample t-test. Department of Bioengineering Proposed Deliverables/Findings: • Comparison of HCO3- pKa to accepted values • Titration curves for all titrations • dB/dpH curves (numerical differentiation) to determine pKa’s and buffer capacities • T-test results: It is expected that P<0.05, i.e. no significant difference Below: sample titration and dB/dpH curves Standardization of HCl with Na2CO3 dB/dpH vs. pH of buffer 12.000 pH 8.000 Trial 1 Trial 2 6.000 4.000 2.000 0.000 0 0.005 0.01 0.015 0.02 0.025 HCl added (mol) Department of Bioengineering 0.03 dB/dpH 10.000 0.05 0.045 0.04 0.035 0.03 0.025 0.02 0.015 0.01 0.005 0 0.000 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 2.000 4.000 6.000 8.000 pH 10.000 12.000 14.000 Potential Pitfalls: • Anticoagulants may affect pH and buffering capacity of guinea pig blood, e.g. citrate is an ionic form of citric acid • 25mM of bicarbonate in the blood is an approximation; exact value ranges from 21-28mM1 • Blood contains other substances and buffering agents that may cause its buffering capabilities to slightly differ from pure bicarbonate • Difficulty in storage of blood samples, which may affect its properties ALTERNATIVES: • Use artificial blood alternatives (would not truly represent real blood) • Purchase serum only, which does not contain cells, clotting factors, or anticoagulants (or purchase plasma or whole blood without anticoagulants, or with only those anticoagulants known to have no effect) • Purchase blood as late as possible 1 http://www.edu.rcsed.ac.uk/lectures/lt8.htm Department of Bioengineering Equipment/Materials and Budget & Justification: EQUIPMENT • pH meter & pH 4, 7, 10 standards • 50 mL burette and stand • 200 mL beakers • Magnetic stirrers/stir bars SUPPLIES • 1M HCl standard • Reagent grade anhydrous Na2CO3 • Gloves NEWLY PURCHASED SUPPLIES/EQUIPMENT Guinea Pig whole blood: chosen for price, feasibility (mammilian), and safety Cost- 1,000mL x $170/100mL = $1,700 (50mL for 20 lab groups) Supplier- Lampire Biological Laboratories (www.lampire.com) Department of Bioengineering