Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
advertisement

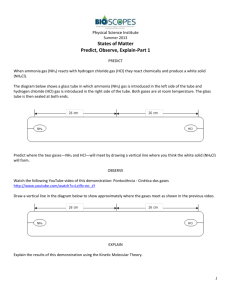
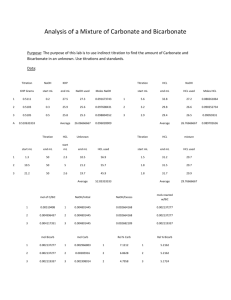
Exam 2 Review Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Lindsey and Elizabeth CHEM 178 Schewe-Miller and Bonnacorsi 3/8/15 1. Which of these conjugate acid-base pairs will NOT function as a buffer? a. CH3COOH and CH3COOb. HCl and Clc. HCO3- and CO32d. All of the above will function as a buffer 2. Which of the following is a Lewis acid, but not a Bronsted acid? a. HCl b. BBr3 c. NH3 d. KOH e. CH4 3. What is the pH of a 0.03 M solution of Ba(OH)2? a. 1.52 b. 12.48 c. 1.22 d. 12.78 e. 0.03 4. Which one of the following binary compounds would you expect to be the most acidic? a. NaH b. CH4 c. SnH4 d. H2O e. H2S 5. What is the pH of a 0.15 M HCl solution at the start of its titration with 0.15 M NaOH? a. 0.15 b. -0.15 c. 0.82 d. -0.82 e. 13.2 6. Which occur(s) when HCl is added to an aqueous buffer solution containing ammonia and ammonium chloride? a. pH of the solution decreases b. More NH4+ forms c. Less NH3 exists d. Less OH- exists e. All of the above 7. The pH of a 0.15 M weak base B is 9.25. What is Kb for B? a. 1.3x10-10 b. 2.11x10-9 c. 6.25x10-8 d. 2.39x10-7 e. 6.92x10-3 8. What is the equivalence point pH of the solution formed by the titration of 50 mL of 0.15 M CH3COOH using 25 mL of 0.3 M NaOH? a. 3.22 b. 4.53 c. 7.00 d. 8.26 e. 8.88 9. Which of the following solutions is a buffer? a. 0.1 M HCl and 0.1 M NaCl b. 0.1 M NH4Cl and 0.1 M NaCl c. 0.1 M NH4Cl and 0.1M CH3COOH d. 0.1 M NH3 and 0.1 M NH4Cl 10. When hydrogen chloride reacts with ammonia, ammonium chloride is formed. Which is the Lewis acid and which is the Lewis base? HCl + NH3↔NH4Cl 11. Using the following titration of 0.050 L of a 0.100 M HBr acid solution using 0.250 M NaOH. a. What is the pH before the titration begins? b. What is the pH after 50.00 mL of NaOH is added? 12. Calculate the concentration of an aqueous solution of Ca(OH)2 that has a pH of 10.05 13. Circle the stronger acid: a. HClO3 b. HBr c. PH3 d. HNO3 HClO4 HF H2S HNO2 14. Will the following solutions be acidic, basic or neutral? a. Ba(CH3COO)2 b. NH4Cl c. Al(ClO4) d. NaCl 15. Calculate the pH of the solution formed when 45 mL of 0.100M NaOH is added to 50 mL of 0.100M CH3COOH (Ka = 1.8 x 10-5) 16. Sketch a graph of what this titration would look like. Label the axes, equivalence points, buffer zones (with the buffer components), and the equivalence volumes. 17. How does the titration curve of a strong acid and strong base differ from a weak acid and a strong base?