Earthquakes and Volcanoes Study Guide
advertisement

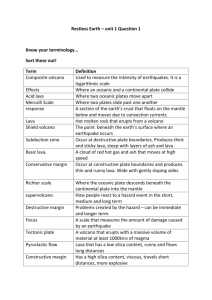
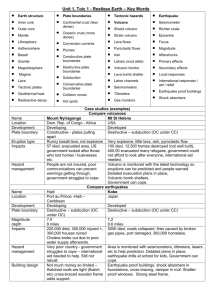
Earthquakes and Volcanoes Study Guide Faults Normal Fault: Plate boundary- divergent Stress- Reverse Fault: Plate boundary- convergent Stress- tension compaction Strike-slip Fault: Plate boundary- transform Stress- shear Seismic Waves P waves: Primary waves Come first Back and forth motion Travel through Solids and Liquids S waves: Secondary waves Sideways or side to side motion Travel through solids only Surface waves: Waves on Earth’s surface Cause the most damage Circular movement Focus/Epicenter Focus: Starts Right deep within the earth along the fault line where the rupture occurs Epicenter: Point Earth directly above the focus, on the surface of the Hot Spots Areas on Earth’s mantle where high temperature causes sections of Earth to rise Heat melts the rock that is forced to the surface Form away from plate boundaries Examples: Hawaii, Yellowstone Composite Volcano Eruption: Alternate between explosive and non-explosive eruptions Sometimes runny lava, sometime pyroclastic material type lava Wide base/steep sides Most dangerous Alternate between explosive and non-explosive eruptions Most dangerous Cinder Cone Volcano Smallest, but most explosive Lava that breaks up and shoots into the air (pyroclastic material) Magma is viscous Most common volcano Shield Volcano Very wide, but shallow/gradual slope Runny lava Non-explosive Get their name from a warriors shield Ex: Mt. Eta