Classification of Organisms
advertisement

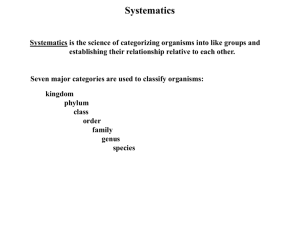
Classification of Organisms Campbell’s Biology Chapters 26-34 TAXONOMY the study of the classification and scientific naming of living things. Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Binomial Nomenclature Musca domestica Homo sapiens Gorilla gorilla Quercus rubra Canis familiaris Felis domesticus Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Prokaryotic Wide range of feeding mechanisms Heterotrophs: • • • • Saprophytes Parasites Commensals Mutualists - Autotrophs Chemosynthetic Photosynthetic Range of Respiratory Mechanisms: Aerobes Facultative Anaerobes Obligate Anaerobes Range of Morphology: Cocci Bacilli Spirilla Strepto Staphylo Range of Reproductive Mechanisms: Transformation Transduction Conjugation Binary Fission Kingdom Archaebacteria OLD! Cell Wall is NOT made of PEPTIDOGLYCAN Well adapted to HARSH environments! Halophiles (in Salton Sea) Methanogens (in sewers, soil, swamps,dig.tracts) Thermoacidophiles (HOT / Acidic ) Kingdom Eubacteria Associated Structures: Peptidoglycan cell wall Plasmids Capsules Flagellen Endospores Gram NEGATIVE vs. Gram POSITIVE Gram Negative: thin cell wall retains saphranin stain ex: Enterobacteria (E. coli) Spirochetes (T. pallidum) Cyanobacteria etc. see notes Gram Positive Thick peptidoglycan cell wall Retain crystal violet stain All heterotrophic! Ex: lactic acid bacteria (dairy products) Streptococci (strept throat, scarlet fever) Staphylococci (skin infections) Clostridia (tetanus, gangrene, botulism) Actinomycetes (leprosy / tuberculosis) Bacterial Infection and disease See Prokaryotes and Disease (Chapter 27) Diseases Caused by Bacteria Tuberculosis Syphilis Mononucleosis Tetanus Pneumonia air droplets sexual transmission air droplets injury air droplets The Others Viruses * Kingdom Protista Kingdom Fungi chapter 18 chapter 28 chapter 31 The Endosymbiont Theory Paramecium caudatum Entamoeba histolytica Trypanosoma Candida albicans http://www.med.sc.edu:85/mycology/thrush.jpg http://www.kcom.edu/faculty/chamberlain/Website/fungi.htm Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Animalia Protista Animalia Evolution of Animals: Protozoans Kingdom Animalia Multicellular Heterotrophic Reproduce sexually Lack cell walls Motile @ some stage in development Rapid response to external stimuli Invertebrate Animal Phyla Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Annelida Mollusca Arthropoda Echinodermata sponges jellyfish flatworms roundworms earthworms snail,clam,octopus insects, spiders, shellfish seastars Vertebrate Animal Phylum Chordata! Chordate Classes Agnatha Chondricthyes Osteicthyes Amphibia Reptilia Aves Mammalia jawless fish sharks, rays bony fish frogs, salamanders snakes, turtles, lizards birds mammals! Mammalian Characteristics Endothermic (warm blooded) Body Hair Mammary Glands! Mammalian Orders Monotremes Marsupials Placental Mammals Body Symmetry Radiata - exhibit radial symmetry - Diploblastic2 layers of tissue form during embryonic development ex: phylum Cnidaria phylum Ctenophora Bilateria Bilateral Symmetry Triploblastic – 3 layers of tissue during embryonic dev. ectoderm (nervous, integ systems,eye) mesoderm (skeletal,muscle,blood,kidney) endoderm (GI / resp. tracts)