Characteristics of & Classification of Life
advertisement

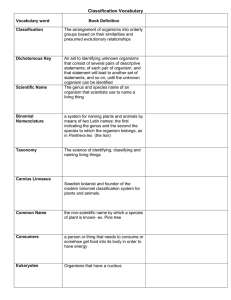
Characteristics of & Classification of Life What are living things? What are the characteristics of life? Organism= a living thing Animals, plants, fungi, microbes, etc. Death is NOT nonliving b/c to die, one has to live first To be considered living, a thing must: 1) need/use food & H2O—energy 2) composed of cells 3) reproduces/makes more of its kind 4) exchange gases (CO2 & O2) 5) grow & change over a life time 6) move! 7) React to the environment 8) DIE! Have a finite life span 9) Adapt/evolve over time or go extinct 10) Excrete wastes 11) Composed of the same basic chemicals: H2O, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, & nucleic acids 12) Can heal itself What are the basic principles of biology? What is biological classification? What are the levels of biological classification? 13) Maintain homeostasis= balanced internally: mess w/homeostasis & u die! The “big ideas” that connect the study of life: 1) living things are VERY different from e@ other, but strangely the same 2) organisms evolve-change over a loooooong time! 3) Structure & function are complementary—how it’s built, enables it to do its job effectively 4) Chemistry & physics work the same in life and non life Biological classification= organizing living things so they are easier to study Taxonomy= the study of biological classification Organisms are grouped according to cell type, # of cells & how it gets food 1) Domain: 3 domains Bacteria Archaea: prokaryotes= unicellular organism w/out a nucleus—DNA floats freely Eukarya: eukaryotes= cells w/ DNA enclosed in a nucleus 2) Kingdom: 4 eukaryotic kingdoms Protists=most are unicellularslime molds, algae/kelp, amoeba, diatoms, paramecium Fungi= decomposers-molds, yeast, mushrooms, puffballs Platae= multicellular autotrophs= make their own food Animalia= multicellular heterotrophs= must search for food 3) Phylum: (phyla is plural) 2 plant kingdom phyla 9 animal kingdom phyla 4) Class: many classes in e@ phyla What did I learn from the video “Animal Classification” 5) Order: many orders in e@ class 6) Family: many families in e@ order 7) Genus: (genera) several genera in e@ family 8) Species: individual organism, a few species in e@ genus Things can make offspringhorse + donkey=mule “Kids prefer candy over fancy green salads” Aristotle created the first classification system Over 3.5 million known organisms Common names are NOT used by everyone b/c of differing languages Latin is the language of science b/c it’s a “dead” language so it doesn’t change Species are individual organisms & do not look like any other organism Linnaeus created the modern classification system Classification starts out broad and narrows to specific organisms Name for man is “homo sapiens” Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species