click
advertisement
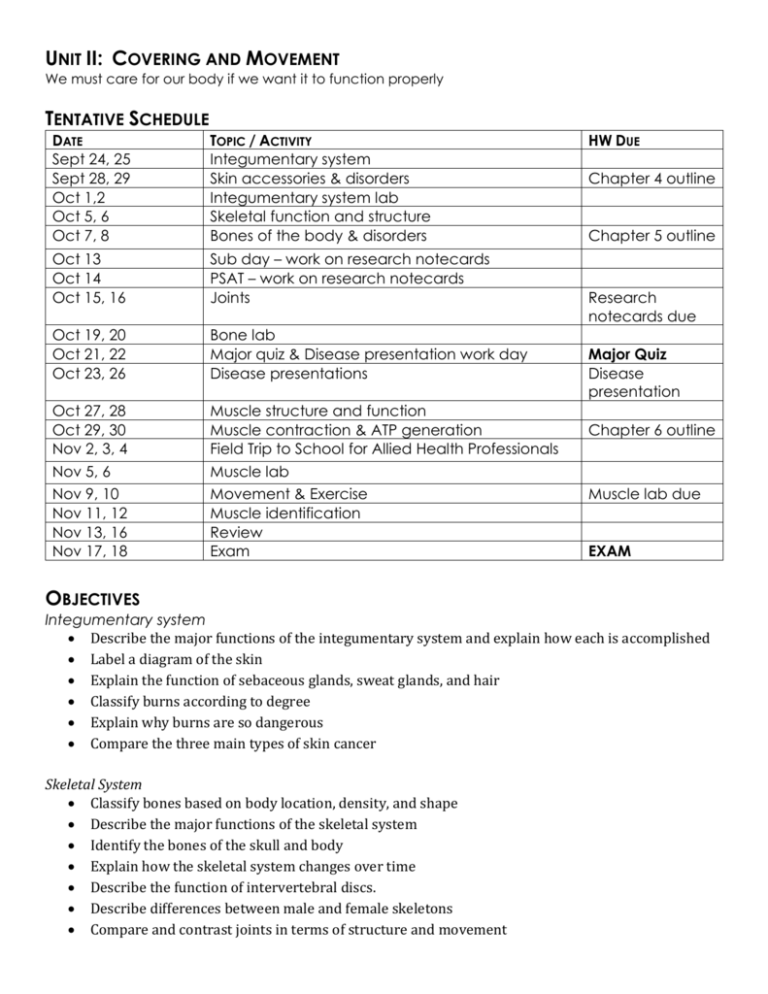
UNIT II: COVERING AND MOVEMENT We must care for our body if we want it to function properly TENTATIVE SCHEDULE DATE Sept 24, 25 Sept 28, 29 Oct 1,2 Oct 5, 6 Oct 7, 8 TOPIC / ACTIVITY Integumentary system Skin accessories & disorders Integumentary system lab Skeletal function and structure Bones of the body & disorders Oct 13 Oct 14 Oct 15, 16 Sub day – work on research notecards PSAT – work on research notecards Joints Oct 19, 20 Oct 21, 22 Oct 23, 26 Bone lab Major quiz & Disease presentation work day Disease presentations Oct 27, 28 Oct 29, 30 Nov 2, 3, 4 Nov 5, 6 Nov 9, 10 Nov 11, 12 Nov 13, 16 Nov 17, 18 Muscle structure and function Muscle contraction & ATP generation Field Trip to School for Allied Health Professionals Muscle lab Movement & Exercise Muscle identification Review Exam HW DUE Chapter 4 outline Chapter 5 outline Research notecards due Major Quiz Disease presentation Chapter 6 outline Muscle lab due EXAM OBJECTIVES Integumentary system Describe the major functions of the integumentary system and explain how each is accomplished Label a diagram of the skin Explain the function of sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and hair Classify burns according to degree Explain why burns are so dangerous Compare the three main types of skin cancer Skeletal System Classify bones based on body location, density, and shape Describe the major functions of the skeletal system Identify the bones of the skull and body Explain how the skeletal system changes over time Describe the function of intervertebral discs. Describe differences between male and female skeletons Compare and contrast joints in terms of structure and movement Describe the cause and symptoms of disorders of the skeletal system, including arthritis and osteoporosis Muscular System Compare the structure and function of the three types of muscle Label diagram of skeletal muscle Describe the events that occur during muscle stimulation and contraction Describe three ways in which ATP is regenerated within muscle tissue Describe the effects of exercise on muscles Describe types of body movement Identify major muscles of the body VOCABULARY Integumentary Epithelial membrane Cutaneous membrane Mucous membrane Serous membrane Peritoneum Pleura Pericardium Synovial membrane Keratinization Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum Skeletal Axial Appendicular Compact bone Spongy bone Long bones Short bones Flat bones Irregular bones Diaphysis Melanin Papillary layer Reticular layer Carotene Exocrine gland Sebaceous gland Sebum Sweat gland Arrector pili Rule of nines First degree burn Second degree burn Third degree burn Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Melanoma Periostenum Epiphyses Epiphyseal line Ephyseal plate Medullary cavity Osteocytes Lacunae Lamellae Haversian canals Canaliculi Volkmann’s canals Osteoblast Osteoclast Fibrous joint Syndesmoses Cartilaginous joint Synovial joint Bursae Tendon Muscular Endomysium Perimysium Epimysium Aponeuroses Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Sarcolemma Myofibrils Sarcomeres Myofilaments Myosin Actin Sarcoplasmic reticulum Neuromuscular junction Synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine Action potential Graded response Tetanus Creatine phosphate Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration Glycolysis Ligament Plane joint Hinge joint Pivot joint Condyloid joint Saddle joint Ball & socket joint Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Lactic acid Muscle fatigue Oxygen debt Muscle tone Endurance Resistance Origin Insertion Flexion Extension Rotation Abduction Adduction Circumduction Dorsiflexion Plantar flexion Inversion Eversion Supination Pronation Opposition Prime mover Antagonist Synergist Fixator