PowerPoint - Hess's Law Calculations and Enthalpy Diagrams
advertisement

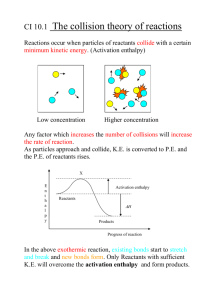
Hess’s law • Hess’s Law states that the heat of a whole reaction is equivalent to the sum of it’s steps. • For example: C + O2 CO2 The book tells us that this can occur as 2 steps C + ½O2 CO H = – 110.5 kJ CO + ½O2 CO2 H = – 283.0 kJ C + CO + O2 CO + CO2 H = – 393.5 kJ I.e. C + O2 CO2 H = – 393.5 kJ • Hess’s law allows us to add equations. • We add all reactants, products, & H values. • We can also show how these steps add together via an “enthalpy diagram” … Steps in drawing enthalpy diagrams 1. Balance the equation(s). 2. Sketch a rough draft based on H values. 3. Draw the overall chemical reaction as an enthalpy diagram (with the reactants on one line, and the products on the other line). 4. Draw a reaction representing the intermediate step by placing the relevant reactants on a line. 5. Check arrows: Start: two leading away Finish: two pointing to finish Intermediate: one to, one away 6. Look at equations to help complete balancing (all levels must have the same # of all atoms). 7. Add axes and H values. C + ½O2 CO CO + ½O2 CO2 H = – 110.5 kJ H = – 283.0 kJ CO2 H = – 393.5 kJ C + O2 C + O2 Reactants Products Enthalpy Intermediate H = – 110.5 kJ CO + ½O2 H = – 393.5 kJ H = – 283.0 kJ CO2 Note: states such as (s) and (g) have been ignored to reduce clutter on these slides. You should include these in your work. Practice Exercise with Diagram Draw the related enthalpy diagram. C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) H= –1411.1 kJ 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) H= +1367.1 kJ Intermediate H = – 1411.1 kJ Reactants Products Enthalpy C2H4(g) + H2O(l) C2H5OH(l) H= – 44.0 kJ C2H4(g) + H2O(l) + 3O2(g) C2H5OH(l)+ 3O2(g) H= H = +1367.1 kJ 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) – 44.0 kJ GeO(s) Ge(s) + ½ O2(g) H= + 255 kJ Ge(s) + O2(g) GeO2(s) H= – 534.7 kJ GeO(s) + ½ O2(g) GeO2(s) H= – 279.7 kJ Reactants Products Enthalpy Intermediate H = – 534.7 kJ Ge(s) + O2(g) H = +255 kJ GeO(s) + ½ O2(g) GeO2(s) H= – 280 kJ NO(g) ½ N2(g) + ½ O2(g) H= – 90.37 kJ ½ N2(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) H= + 33.8 kJ H= – 56.57 kJ NO(g) + ½ O2(g) NO2(g) NO + ½ O2(g) Intermediate H = – 90.37 kJ Products Enthalpy Reactants NO2(g) H = +33.8 kJ ½ N2(g) + O2(g) H= – 56.6 kJ Hess’s law We may need to manipulate equations further: 2Fe + 1.5O2 Fe2O3 H=?, given Fe2O3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO2 H= – 26.74 kJ CO + ½O2 CO2 H= –282.96 kJ 1: Align equations based on reactants/products. 2: Multiply based on final reaction. 3: Add equations. 2Fe + 3CO2 Fe2O3 + 3CO H= + 26.74 kJ CO + ½O2 CO2 H= –282.96 kJ 3CO + 1.5O2 3CO2 H= –848.88 kJ 2Fe + 1.5O2 Fe2O3 H= –822.14 kJ Don’t forget to add states For more lessons, visit www.chalkbored.com