AP Chem - Chapter 2: Review Name: Date: _____ Ions and Ionic
advertisement

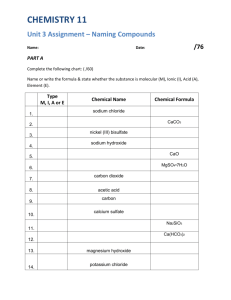
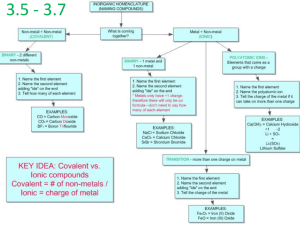
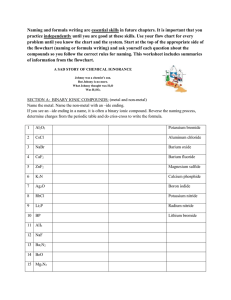
AP Chem - Chapter 2: Review Ions and Ionic Compounds Name: ________________________________ Date: _____ 1. During the formation of an ion, what subatomic particle is removed or added to a neutral atom? 2. Define and give examples of each of the following: a. Cation b. Anion c. Polyatomic Ion 3. Noble gases are stable and do not easily ionize because they have an electron configuration that is stable. Based on this information, provide an explanation of why oxygen most commonly gains two electrons to form a -2 anion, and why sodium most often loses one electron to form a +1 cation. 4. What is an ionic compound? How is it formed? 5. How are molecular compounds different from ionic compounds? Naming Inorganic Compounds 1. What are the rules for naming cations? List three examples of each rule. 2. What are the rules for naming anions? List three examples of each rule. 3. What are the rules for naming ionic compounds? List two examples of each rule. 4. What the rules for naming acids? List two examples of each rule. 5. What are the rules for naming binary molecular compounds? List two examples of each rule. AP Chem - Chapter 2: Review Simple Organic Compounds Name: ________________________________ Date: _____ 1. Define the following: a. Hydrocarbon b. Alkane c. Alcohol Practice: If the name of the compound is given, write the formula. If the formula of the compound is given, write the name. 1. lead(II) nitrate 2. sodium carbonate 3. potassium iodide 4. AgNO3 5. barium nitrate 6. Na2SO3 7. potassium carbonate 8. sodium nitrate 9. barium acetate 10. hydrogen peroxide 11. potassium bisulfate 12. Ba(OH)2 13. Fe3(PO4)2 15. aluminum sulfate 16. calcium hydroxide 17. tin(II) oxide 18. aluminum bicarbonate 19. sodium perchlorate 20. copper(I) dichromate 21. potassium selenide 22. sodium phosphate 23. Fe(ClO)2 24. copper(II) nitrate 25. potassium hypochlorite