Ch. 21 East versus West: A Global Divide and a Cold War
advertisement

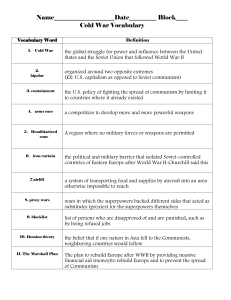
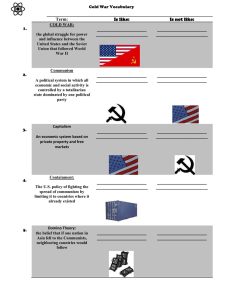
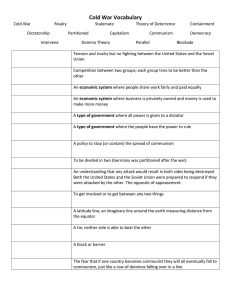
Ch. 21 East versus West: A Global Divide and a Cold War Chelsea Jeanson-Ham Social Studies Education Minnesota Standards • 13. Post-World War II geopolitical reorganization produced the Cold War balance of power and new alliances that were based on competing economic and political doctrines. (The World After World War II: 1950-1989) • 22. Post-World War II United States was shaped by an economic boom, Cold War military engagements, politics and protests, and rights movements to improve the status of racial minorities, women and America’s indigenous peoples. (Post- World War II United States: 1945-1989) • 2. Historical inquiry is a process in which multiple sources and different kinds of historical evidence are analyzed to draw conclusions about how and why things happened in the past. Learning Objectives The students will: • Analyze the primary document • Identify the strengths and weaknesses of each side • Outline the goals of the U.S and Soviet Union • Describe the major events • Understand the outcome of the cold war and its lasting effects 1. Who's side are they from? 2. What is the message? 3. Why might that be important to their war effort? The Beginnings • Communist regimes brought revolutionary change • Launched global conflict • Western capitalist fear communism • Allies during WWII • Major powers • Opposing views of history, society, and international relations http://tropico.wikia.com/wiki/Cold_War Military Conflict and the Cold War • Soviet asserts control in Eastern Europe, but U.S and G.B want open and democratic societies that will be part of capitalist economy • NATO • Warsaw Pact • “Iron Curtain” – divide in Berlin http://resourcesforhistoryteachers.wikispaces.com/file/view/cold_war_mp.jpg/30572399/480x349/cold_war_mp.jpg Document: Churchill's “Iron Curtain Speech” 1. Why does Winston Churchill feel that he can speak freely to the audience? 2. How did the two sides of the iron curtain differ from each other? 3. What is his tone? 4. Based on his speech what should be the next step the U.S takes? 5. What is his opinion of Russia? How does this differ from what we think of today? http://quotesnsmiles.com/picture-quotes/images-20-winston-churchill-picture-quotes-to-motivate-success/ Communism extends to Asia • China • Mao • Korea • North invades south in 1950 • American and Chinese involvement • Still divided • Vietnam • Efforts to unify by communists • Massive American invasion • Protest at home • “Hot wars” • America fears domino effect • Afghanistan http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/ macarthur/maps/koreatxt.html http://www.fasttrackteaching.com/burns/Unit_11_Cold_War/U11_Cold_War_Conflicts.html Cuban Missile Crisis Fidel Castro came to power in 1959 U.S pressure pushed closer to soviets Considered revolution Marxist Win for soviets – no army needed Nikita Khrushchev secretly deployed missiles to Cuba to stop U.S intervention • Americans blockade island – invasion • Fear of nuclear exchange • Compromise between Kennedy and Khrushchev • • • • • http://www.newyorker.com/news/news-desk/castros-defining-crisis Nuclear Standoff and Third World Rivalry Arms race for nuclear weapons 60,000 warheads More accurate Small amount could reduce a major city to rubble, chaos, and possible extinction • Both sides aware – avoid • Both try to attract countries with military and economic aid, educational opportunities, political pressure, and covert action. • • • • http://classroom.synonym.com/after-cold-war-did-nuclear-weapons-soviet-union-possessed-go-21842.html Duck and Cover! The Cold War and the Superpowers - America • Emergence of America as global super power • Containment • “Imperial” presidency and “National Security state” • Increasing middle class • Productive economy • Sent capital abroad 19 billion to 81 billion in 1965 • Culture spread globally http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/newsbysector/retailandconsumer/8279130/McDonalds-the-early-years.html?image=5 The Cold War and the Superpowers – Soviet • Emphasis on military and defense industries • Propaganda vilifies U.S • More conflict • Invade Hungary and Czechoslovakia • Suppression of reforms gave credit to the other side • Triumph in Vietnam https://history.state.gov/milestones/1961-1968/soviet-invasion-czechoslavkia Paths to the End of Communism • Mao dies in 1976 • Mikhail Gorbachev came to power in 1985 • Disintegrate Soviet Union in 1991 • Stagnant economies • Violence http://www.historytoday.com/richard-cavendish/death-joseph-stalin • • • • Stalin's terror Pg 1076-1078 What did people experience? Why might he use these tactics? China: Abandoning Communism and Maintaining the Party • Deng Xiaoping becomes leader • Wants political stability and economic growth • Dismantle collectivized farming and return to small scale • State enterprises given more authority • Welcomed foreign investment • Produce food, clothing, and building materials • Massive corruption, overcrowding, pollution, etc. The Soviet Union: The Collapse of Communism and the Country http://ias.umn.edu/2014/11/06/kuftinec/ • Tackle economic stagnation, black markets, apathy, and cynicism • Freeing enterprises, cooperatives, private farming, some foreign investment • Glasnost policy – cultural and intellectual freedom • Gorbachev makes cuts in forces and negotiations with U.S • Further decline • Democracy movement • 1989 miracle year Conclusions • • • • • • Ending to 45 years of war Goals of both sides Communism shrinks North Korea today Opening with Cuba Contradictions