Word Wall/Vocabulary List
advertisement

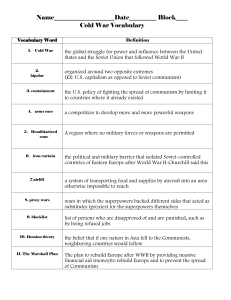
Word Wall/Vocabulary List For Communism and Containment & The Marshall Plan Communism Political theory advocating community ownership of all property, the benefits of which are to be shared by all according to their needs. Containment Strategic foreign policy pursued by the United States in the late 1940s and the early 1950s in an attempt to keep the Soviet Union and communism from spreading. Expansionism Policy adopted by the Soviet Union whose goal was to spread the ideals of communism and add to their territory Alliance A formal agreement between two or more states for mutual support in case of war Ratification To formally approve and sanction Coup d’état A sudden decisive exercise of force in politics; especially : the violent overthrow or alteration of an existing government by a small group Appeasement To bring about peace, sometimes by concessions that sacrifice the principles of the peacemaker Cold War The open yet restricted rivalry that developed after World War II between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies Coercion Domination by force North Atlantic Treaty Organization military alliance established by the North Atlantic Treaty of April 4, 1949, which sought to create a counterweight to Soviet armies stationed in central and eastern Europe after World War II. Point Four Program U.S. policy of technical assistance and economic aid to underdeveloped countries, so named because it was the fourth point of President Harry S. Truman's 1949 inaugural address Truman Doctrine Pronouncement by U.S. Pres. Harry S. Truman on March 12, 1947, declaring immediate economic and military aid to the governments of Greece and Turkey. The United States feared these countries were in danger of falling under Soviet influence if they did not receive this aid. United Nations International organization established on October 24, 1945. The UN aims to maintain peace and security throughout the world and encourage worldwide cooperation on the solving of problems. Marshall Plan U.S.-sponsored program designed to rehabilitate the economies of 17 European countries in order to create stable conditions in which democratic institutions could survive






![The Cold War [1945-1991]: An Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/017625117_1-e9c48b8702d240bbf3e4177b59399df7-300x300.png)