Integumentary System
advertisement

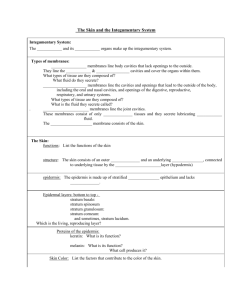
Skin and its appendages – Hair – Nails – Sebaceous glands – Sweat glands Integumentary means “covering” 3,000 square inches of surface area 1. Covering 2. Regulate body temperature 3. Manufacture Vitamin D 4. Nerve receptors 5. Temporary storage 6. Screen-out ultraviolet radiation 7. Special absorptive properties Epidermis – Outermost covering – Avascular Dermis – True skin – Connective tissue – Vascular © 2014 Cengage Learning. 1. Keratinocytes 2. Merkel cells 3. Melanocytes 4. Langerhans cells Stratum corneum Stratum lucidum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale (basement membrane) Also called corium Thicker, inner layer of the skin Many nerve receptors Blood vessels and heat regulation Also called hypodermal layer Lies under dermis Not a true part of the integumentary system Attaches integumentary system to the surface muscles underneath 1. Name three functions of the skin 2. What are the two main layers of the skin? (what is the third layer that is not considered part of the integumentary system?) 3. What is one difference between the epidermis and the dermis? Root shaft Outer cuticle layer Cortex Inner medulla Hair follicle Arrector pili muscle © 2014 Cengage Learning. Hard structures covering the dorsal surfaces of the last phalanges of the fingers and toes Nail bed or matrix Diseases and nail color © 2014 Cengage Learning. Also called sudoriferous glands Perspiration is 99% water Perspiration is excreted through pores Under the control of the nervous system 500 ml water lost per day through the skin Ceruminous or wax glands Secrete sebum which is thick, oily substance Sebum lubricates the skin, keeping it soft and pliable Intact skin is the best way to protect against pathogens Most skin bacteria are associated with hair follicles and sweat glands Hand washing Most effective action to prevent spread of disease ▪ 20 seconds for washing hands ▪ 2-4 minutes for infectious material Becomes more fragile and dry Loss of elasticity Less effective body temperature control Melanocytes decrease Physiological changes can impact self-worth 1. What is the role of the sebaceous glands? 2. Through what layer(s) of the skin do hair follicles reside? 3. What are two characteristics of aging skin? Acne vulgaris – Common and chronic disorder of sebaceous glands Athlete’s foot – Contagious fungal infection Dermatitis – Inflammation of the skin Eczema – Acute or chronic, noncontagious inflammatory skin disease Impetigo – Acute, inflammatory, and contagious skin disease Psoriasis – Chronic inflammatory skin disease (reddish patches covered by silvery-white scales) Ringworm – Highly contagious fungal infection Urticaria (hives) – Intensely itching wheals or welts Boils (carbuncles) – Painful, bacterial infection of the hair follicles or sebaceous glands Rosacea – Common inflammatory disorder (chronic redness and irritation to the face) Herpes – Viral infection that is usually seen as a blister Genital herpes – Virus that may appear as a blister in the genital area Shingles (herpes zoster) – Skin eruption due to a viral infection of the nerve ending Head lice – Parasitic insects Ingrown nails – Common nail problem Fungal infections – Infections of the nail Warts – Viral infections that affect the skin surrounding or underneath the nail Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Malignant melanoma Skin and sun exposure Rule of nines First-degree burns Second-degree burns Third-degree burns Pressure ulcer (decubitus ulcers) – Stage I – Stage II – Stage III – Stage IV 1. Explain what the “rule of nines” is: 2. Pick two skin disorders (not any type of herpes) and explain what each one does to the skin. 3. Within the powerpoint the term “dorsal surface” was used, what does the term “dorsal” mean?