13 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
advertisement

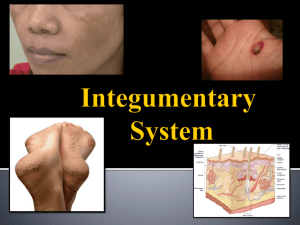
Fluid Balance Balance: Fluid Balance: Electrolyte Balance: When the water coming into the body precisely equals the water being lost by the body each day. Gains and losses of electrolytes are equal. Acid-base balance: When the production of H+ is precisely offset by H+ loss and/ or HCO3- production. Overall body composition: Ionic composition of body fluids: Electrolyte balance: Acid-base balance Respiratory acid-base regulation Metabolic acid-base regulation The Integumentary System: An Overview Integumentary system functions: Protection Excretion Temperature maintenance Nutrient storage Vitamin D3 synthesis Sensory detection The integumentary system consists of Cutaneous membrane Epidermis Dermis Accessory structures Subcutaneous layer The Components of the Integumentary System Thin Skin and Thick Skin The epidermis is composed of layers of keratinocytes Thin skin = four layers (strata) Thick skin = five layers The epidermis Provides mechanical protection Prevents fluid loss Keeps microorganisms from invading the body Layers of the epidermis: Stratum germinativum Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum (found in thick skin only) Stratum corneum The Epidermal Ridges of Thick Skin Figure 5.3 Epidermal characteristics: Cells accumulate keratin and eventually are shed Epidermal ridges are interlocked with dermal papillae Fingerprints Improve gripping ability Langerhans cells (immunity) in s. spinosum Merkel cells (sensitivity) in s. germinativum The Structure of the Epidermis Skin color depends on Blood supply Carotene and melanin Melanocytes produce melanin and protect from UV radiation Epidermal pigmentation Interrupted blood supply leads to cyanosis Melanocytes Epidermal cells Synthesize vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) when exposed to UV Respond to epidermal growth factor Growth Division Repair Secretion Dermal Organization Papillary layer Contains blood vessels, lymphatics, sensory nerves of epidermis Reticular layer Contains network of collagen and elastic fibers to resist tension Dermal Circulation and innervation Cutaneous plexus arteries found in subcutaneous layer/ papillary dermis Cutaneous sensory receptors (light touch, pressure) Stretch marks Caused by excessive stretching of the dermis Patterns of collagen and elastic fibers form lines of cleavage Lines of Cleavage of the Skin Hypodermis Stabilizes skins position against underlying organs and tissues Hairs Originate in hair follicle Composed of root and shaft Root base (hair papilla) surrounded by hair bulb and root hair plexus Hairs have soft medulla and hard cortex Cuticle = superficial dead protective layer Hair types Vellus hairs (peach fuzz) Terminal hairs ( heavy) Club hair (cessation of growth) Shed and grow according to hair growth cycle Arrector pili muscle attaches to hair The Anatomy of a Single Hair Hair Follicles Glands in the skin Sebaceous (oil) Suderiferous (sweat) Mammary Ceruminous Sebaceous glands Discharge waxy sebum onto hair shaft when associated with hairs Sebaceous follicles discharge onto epidermal surface Sebaceous Glands and Follicles Suderiferous glands Apocrine sweat glands Produce odorous secretion Merocrine (eccrine) sweat gland Sensible perspiration Figure 5.12 Sweat Glands Figure 5.12a, b Other glands Mammary glands Structurally similar to apocrine sweat glands Ceruminous glands In ear, produce waxy cerumen Nails Nail body covers the nail bed Nail production occurs at the nail root Eponychium (cuticle) overlies root Free edge of nail extends over hyponychium The Structure of a Nail Injury and repair Regenerates easily Regeneration process includes formation of Scab Granulation tissue Scar tissue Integumentary Repair Integumentary Repair With age Integument thins Blood flow decreases Cellular activity decreases Repairs occur more slowly