Chapter 6 The Skin and the Integumentary System - Svetz-wiki
advertisement
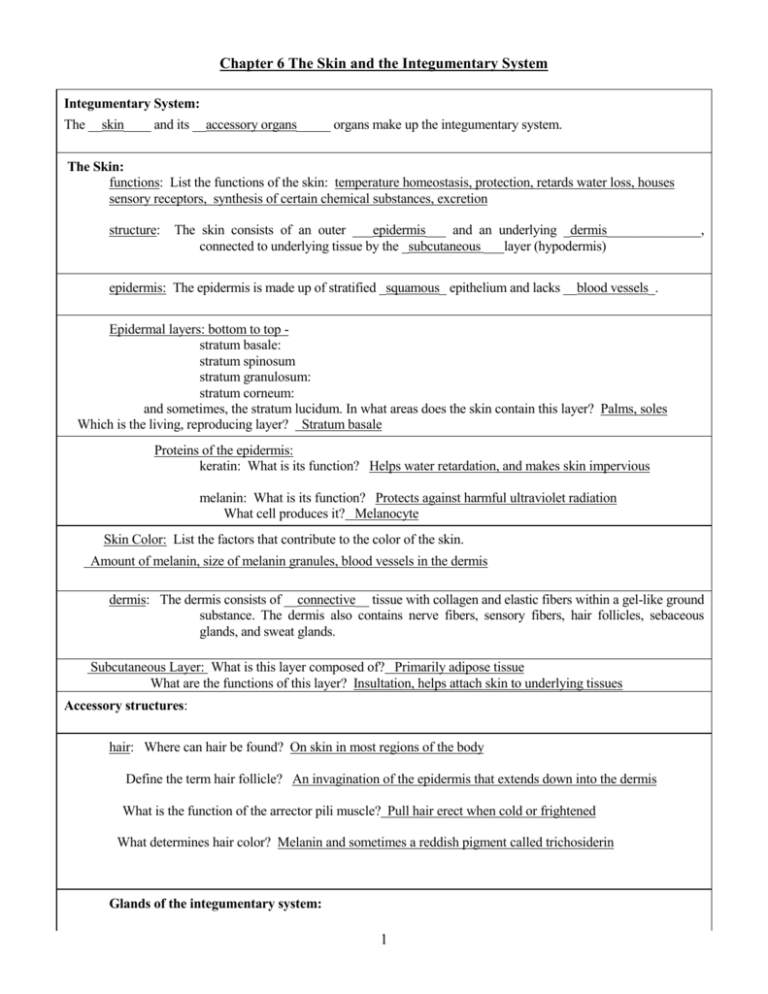
Chapter 6 The Skin and the Integumentary System Integumentary System: The __skin____ and its __accessory organs_____ organs make up the integumentary system. The Skin: functions: List the functions of the skin: temperature homeostasis, protection, retards water loss, houses sensory receptors, synthesis of certain chemical substances, excretion structure: The skin consists of an outer ___epidermis___ and an underlying _dermis______________, connected to underlying tissue by the _subcutaneous ___layer (hypodermis) epidermis: The epidermis is made up of stratified _squamous_ epithelium and lacks __blood vessels_. Epidermal layers: bottom to top stratum basale: stratum spinosum stratum granulosum: stratum corneum: and sometimes, the stratum lucidum. In what areas does the skin contain this layer? Palms, soles Which is the living, reproducing layer? Stratum basale Proteins of the epidermis: keratin: What is its function? Helps water retardation, and makes skin impervious melanin: What is its function? Protects against harmful ultraviolet radiation What cell produces it? Melanocyte Skin Color: List the factors that contribute to the color of the skin. Amount of melanin, size of melanin granules, blood vessels in the dermis dermis: The dermis consists of __connective__ tissue with collagen and elastic fibers within a gel-like ground substance. The dermis also contains nerve fibers, sensory fibers, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. Subcutaneous Layer: What is this layer composed of? Primarily adipose tissue What are the functions of this layer? Insultation, helps attach skin to underlying tissues Accessory structures: hair: Where can hair be found? On skin in most regions of the body Define the term hair follicle? An invagination of the epidermis that extends down into the dermis What is the function of the arrector pili muscle? Pull hair erect when cold or frightened What determines hair color? Melanin and sometimes a reddish pigment called trichosiderin Glands of the integumentary system: 1 sebaceous glands: What type of glands are they? Holocrine glands What structure are they associated with? Hair follicles What is their secretion called? Sebum sudoriferous glands (sweat glands): appocrine are associated with __sexual arousal_ control and secrete __sweat with characteristic odors________ eccrine are associated with ____temperature control___. ceruminous glands are found in the __ear canal__ and secrete ___wax____ nails: Nails consist of stratified __squamous___epithelial cells overlying the nail bed, with the ___lunula_______ as the most actively growing region of the nail root. Temperature regulation: Proper temperature regulation is vital to maintaining metabolic reactions. The ___skin_____plays a major role in temperature regulation with the ___hypothalamus_ controlling it. Active cells, such as those of the heart and skeletal muscle, produce __heat______. Heat may be lost to the surroundings from the skin. The body responds to excessive heat by __dilation__of dermal blood vessels and _sweating______. The body responds to excessive cooling by ___constriction_ dermal blood vessels, inactivating __sweat_____ glands, and increasing muscle usage through __shivering________________. Healing of Wounds and Burns Inflammation, in which blood vessels ____dilate____ and become more _permeable____, causing tissues to become red and swollen, is the body's normal response to injury. . Superficial cuts are filled in by reproducing _epithelial__ cells. . Deeper cuts are closed off by ___clots__, covered by _scabs, and eventually filled in by __fibroblasts_____, making connective tissue. Large wounds leave scars and healing may be accompanied by the formation of __graulations_____. 2