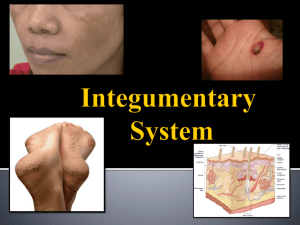
BIOL 430 - LABORATORY #3 Integumentary System References: Text: Chapter 5 Lab Manual: Exercise 5 – The Integumentary System MasteringA&P > Study Area > PAL: - Anatomical Models > Integumentary System - Histology > Integumentary System Pre-Lab Assignments: p. 124-125 Learning Objectives: 1. Identify the tissue, cells and layers of the epidermis. 2. Identify the tissues and layers of the dermis. 3. Identify the glands, muscle and sensory structures of the skin. 4. Identify the anatomical features of the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis from light micrographs. 5. Describe the features of the selected pathologies. Cutaneous membrane Epidermis: Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Cells: Keratinocytes Melanocytes Tactile epithelial (Merkel) cells + free nerve ending = Tactile disc Dendritic cells (Langerhans cells) Layers: Stratum Stratum Stratum Stratum Stratum basale spinosum granulosum lucidum (thick skin only) corneum Thick vs. Thin Skin Differences in # of layers in various strata Presence/absence of stratum lucidum Presence/absence of sebaceous glands and hair Thickness of dermis Dermis: Papillary layer: Areolar connective tissue Dermal papillae – these projections form the epidermal ridges (fingerprints) Blood vessels – Subpapillary plexus Receptors: Refer to Chapter 13 – Table 13.1; p. 491-492 Free nerve endings Free nerve ending associated with Tactile cells – Tactile disc Tactile (Meissner) corpuscles Reticular layer: Dense irregular connective tissue Blood vessels – Dermal vascular (cutaneous) plexus Hair follicles (do not need to know details of hair structure on p. 132) Arrector pili muscle and sebaceous glands associated with hair follicles Glands Sebaceous glands: Ducts generally open into hair follicles Produce sebum Holocrine – mode of secretion Sweat (sudoriferous) glands: Eccrine - Watery secretion – body temperature regulation Ducts open to skin surface Apocrine - Secretions rich in proteins and fats Axillary, nipple, anogenital areas Ducts open into hair follicles (deeper location in dermis compared to eccrine) Merocrine – mode of secretion Receptors: Refer to Chapter 13 – Table 13.1; p. 491-492 Lamellar (Pacinian) corpuscle Hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus) Bulbous corpuscles (Ruffini endings) Hypodermis (Subcutaneous layer): Adipose and Areolar connective tissues Highly vascular