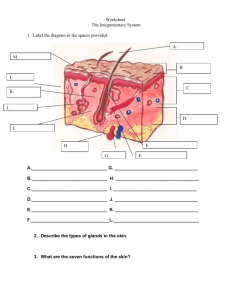
Integumentary System: name for the skin and its structures
advertisement

Integumentary System: name for the skin and its structures. Integumentary System is called a membrane because it covers the body. Integumentary System is called an organ because it contains several kinds of tissues. Integumentary System is called a system because it has organs and other parts that work together for a particular function The skin has 3 layers: Epidermis: outermost layer Dermis: “true skin” Subcutaneous fascia or hypodermis: the innermost layer Epidermis is made of 2 layers with NO blood vessels or nerve cells: Stratum corundum: outermost layer Stratum germinativum: innermost layer Dermis is made of elastic connective tissue and contains blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, involuntary muscle, sweat and oil glands, and hair. Subcutaneous fascia (hypodermis): inner most layer that is made of elastic and fibrous connective tissue and adipose (fatty) tissue, and connects the skin to underlying muscles. The parts of the skin: Sudoriferous glands: sweat glands extend through the dermis and open to the surface Sebaceous glands: oil glands usually open to hair follicles Hair: consist of a root (hollow tube) and a hair shaft. Protects the body and covers all body surfaces except palms and soles of foot. Nails: protect the fingers and toes from injury. Made of dead keratinized epidermal epithelial cells packed closely together to form a thick, dense surface formed in the nail bed. If lost, nails will re-grow if the nail bed is not damaged. Functions of skin: Protection: barrier to the sun’s UV rays and invasion of pathogens (germs), holds moisture in and prevents deeper tissues from drying out. Sensory perception: nerves help the body to respond to pain, pressure, temperature, and touch. Regulation of body temperature: blood vessels in skin dilate (enlarge) to release excess heat and constrict (shrink) to hold in body heat. Storage: temporary storage of fat, glucose, water, vitamins, and salts. Adipose tissue (fat) stores energy. Absorption: substances (medicine) can be absorbed through the skin: transdermal medication Excretion: skin eliminated waste, salt, and excess water and heat: perspiration Production: aides in production of vitamin D (using UV rays) Skin color (pigmentation) is inherited and is determined pigmented cells of the skin: melanin-brownish black pigmentation produced by melanocytes. Carotene: yellowish red pigment aides in skin color also. Albino: absence of skin pigments causing the skin to have a pinkish tint. Hair is pale yellow or white and eyes are red in color and sensitive to light. Abnormal colors: Erythema: red. Caused by burns or congestion of blood vessels Jaundice: yellow: caused by liver or gallbladder disease from bile Cyanosis: blue: caused by insufficient oxygen. Skin eruptions Macules (macular rash) Papules (popular rash Vesicles Pustules Crusts Wheals Ulcer Diseases and abnormal conditions Acne vulgaris Athlete’s foot Skin cancer Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Melanoma Dermatitis Eczema Impetigo Psoriasis Ringworm Verrucae/warts