Cell Differentiation
Cell Differentiation
By Emma Sanderson
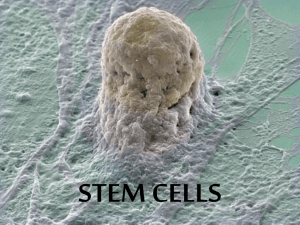
Stem Cell Basics
● Give rise to differentiated cells
● Have 3 properties:
● are able to divide and renew for extended amounts of time
● are unspecialized
● give rise to specialized (differentiated) cells
3 Kinds of Stem Cells
Totipotent: can form all types of cells, including placental cells. Only embryonic cells are totipotent.
Pluripotent: can become cell types of the body.
Pluripotent cells are embryonic stem cells.
Multipotent: are adult stem cells and umbilical cord blood cells. These cells can become more than one cell type.
Can A Stem Cell Switch?
● A stem cell “switch” is called transdifferentiation
● In this case, bone marrow cells “switched” to cheek cells.
● Fusion (when a stem cell binds itself to a differentiated cell) did not occur.
When?
5 women received bone marrow transplants from their brothers. When a team of scientists at NIH were pursuing the possibility of transdifferentiation, they took cheek swabs from these women and found cells containing the male Y chromosome. Also, they found that the sample cells they took showed no signs of fusion.These marrow-to-cheek cells also contained the structural protein cytokeratin, which is found in mucosal cells.
This proved that transdifferentiation does occur outside of a lab-manipulated setting.
The Numbers
Percentage of “switched” cells: 0.8%-12.7%
2/9,700 cells collected could have possibly fused
arizonapain.com
Cheek cells
waynesword.palomar.edu
Works Cited
Scientists Report New Data in Adult Stem Cells Debate., 2003. SIRS Government
Reporter. Web. 29 Sep. 2013
< http://sks.sirs.com
>
"Stem Cell Basics." National Institutes of Health . N.p., n.d. Web. 5 Oct. 2013.
< http://stemcells.nih.gov/info/basics/pages/basics1.aspx
>.
"What is the difference between totipotent, pluripotent and multipotent?"
NYSTEM . N.p., n.d. Web. 5 Oct. 2013. <http://stemcell.ny.gov/faqs/ what-difference-between-totipotent-pluripotent-and-multipotent>.