stem cells - Cloudfront.net
advertisement
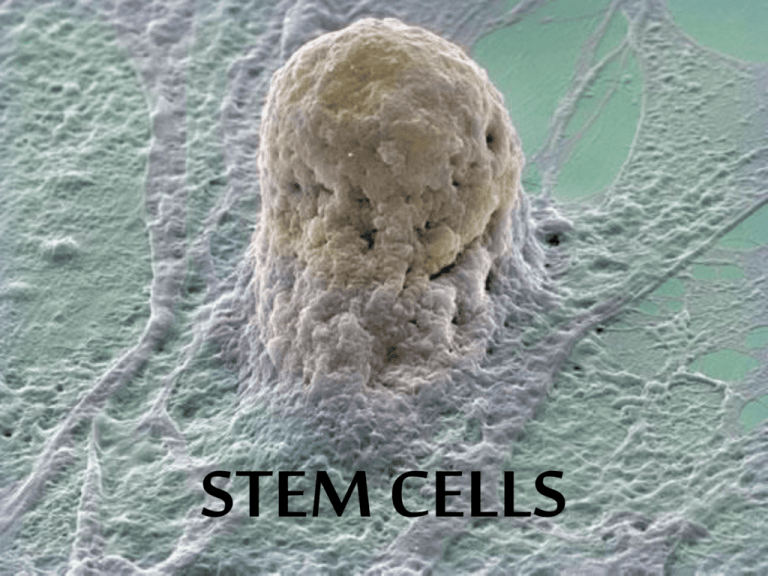
STEM CELLS • Can be any type of cell during early life and growth • Can serve as internal repair system in some tissues • Each new cell after division can remain a stem cell or become a specialized cell ***“What do you notice? What can you draw upon from relating these two images?“*** BRAIN • Totipotent: Having the ability to give rise to all the cell types of the body plus all of the cell types that make up the extraembryonic tissues such as the placenta. • Pluripotent: Having the ability to give rise to all of the various cell types of the body. • Multipotent: Having the ability to develop into more than one cell type of the body • • • • • Early Embryonic = Totipotent Blastocyst = Pluripotent Fetal = Pluripotent Umbilical Cord = Multipotent Adult = Multipotent “Multipotent” • Primary role is to maintain and repair tissue in which they are found • Limited Use “Pluripotent” • Contain the more “sought after” stem cells • Destruction of embryo – “Human Life” – “Right to Choose” • People who have Parkinson's disease experience difficulty with movement, balance and speech. • These problems result from the death of specialized brain cells called dopamine neurons. • These cells produce dopamine, a chemical that helps control muscle movements. • The effects of the disease can be treated with drugs that help increase dopamine in the brain, but there is no known cure. • Researchers studying Parkinson's disease knew that the problem was to replace the dead dopamine neurons with healthy dopamine-producing cells.