File
advertisement

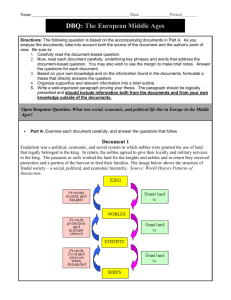
March 6, 2015 • TO-DO – Pick up today’s notes • HOMEWORK – Charlemagne MiniProjects due Monday • GOAL – To understand Feudalism, Manorialism, and why they mattered in the Middle Ages • AGENDA – Make packet – Extra Credit – Notes and videos Extra Credit • Create a relevant, accurate cover sheet for your Middle Ages packet • Due by next Wednesday Aim: How was Europe organized during the Middle Ages? Do Now: While China, India, The Byzantines, and the Islamic Empires were experiencing a golden age, what was going on in Western Europe? For review, briefly describe what happened to western Europe at the end of the Roman Empire. What do you think a dark age is? The Middle Ages Defined • After the fall of Rome, Western Europe entered a period known as the Middle Ages, also known as The Medieval Period, which lasted from around 400 – 1400 C.E. The Middle Ages or Medieval Period 400-1400 500 B.C – 476 A.D The Roman Empire The Renaissance (Rebirth) Begins around 1400 The Middle Ages Defined • In general, the Middle Ages are defined by a lack of central government, decline of trade, population shift to rural areas, decrease in learning, and a rise in the power of The Roman Catholic Church. The Rise of Feudalism – Political and Social Organization of Medieval Europe The Problem: You are one of many kings ruling various kingdoms in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. You are also the proud owner of large landholdings in your area. However, you are struggling to control the nobles in your kingdom who are fighting each other to expand their landholdings and increase their power (in turn, threatening yours). In addition, you are concerned about increasing barbarian attacks from the east. What can you do to create structure in your kingdom and ensure order? Your Solution: The Rise of Feudalism – Political and Social Organization of Medieval Europe Oath of loyalty/military support Loyalty/military King Grant Fief (land) Vassal (Lord) Shelter/food Knights Labor, rent Serfs and Peasants (90% of population) Shelter/food And protection Feudalism The Rise of Feudalism – Political and Social Organization of Medieval Europe • Causes of Feudalism: After the fall of Rome, Western Europe was a scary place! With no strong, central government to raise a large army, there was no protection from invaders. The Feudal system emerged as a means to create social/political order and stability in society as well as to provide a system of protection •The Role of Serfs: They were bound to the land. In other words, slaves. •No social mobility! Your place in this feudal pyramid was determined by birth! The Manor System – The Medieval Economic System • Sometimes the manor system is referred to as manorialism. • The manor was completely self sufficient meaning that everything that was needed was on the manor. • Very little reason to leave or travel beyond your manor. Serfs Knights The Manor System – The Medieval Economic System • The self sufficient manor contributed to the decline of learning. No new ideas were exchanged. Technology was slow to progress. • Little use of money. Wealth based on land. Social Political Religious •Strict social hierarchy based on the feudal pyramid. •Feudalism – Kings and nobles exchange land for loyalty and protection. •Rise in the power of the Pope and Roman Catholic Church •Social Status determined by birth •Lack of social Mobility •Code of Chivalry •Decentralized government •People followed religious Canon Law – Led by Pope •Pope had power of excommunication Intellectual Technological Economic •Manorialism •Decline in learning as population shifts to rural areas •Most people were illiterate •Priests and monks could read and write – wrote books, mostly religious •Technology slow •Manor system – to progress as completely selfexchange of ideas sufficient in that it declines. had everything •Most technology used that was needed for military or farming – Crossbow, armor, longbow, siege weapons, early guns, heavy plough, water and wind mills, mechanical clocks, stirrups, hourglass, glass, printing press •Little use of money •Little to no trade •Pay 10% tithe to church Medieval Castles Medieval Social Structure