Income Statement - Buckeye Capital Investors
advertisement

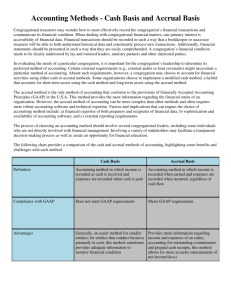
Income Statement Analysis Agenda What is it? B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n Accrual Accounting Line Items Fundamental Analysis and the Income Statement Game Time What is an Income Statement The income statement summarizes the inflows and outflows of money (not necessarily cash) over an accounting period B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n • Inflows = Revenues • Outflows = Expenses Inflow Outflow Outflows Accrual Accounting Why do companies use accrual accounting? B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n • Measures the performance of a company by recognizing economic events regardless of when transactions occur • As opposed to cash accounting where expenses and revenues are recorded when cash is transferred • Accrual accounting uses the Matching Principle • States that all expenses must be matched in the same accounting period as the revenues they help to earn Accrual Accounting Example B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n Month 1: You cater an event where the cost to you was $100. The customer pays you $200 for your services. Month 2: You cater an event where the cost to you is $100. The customer agrees to pay you $200 next month Revenue Expense Profit Cash Accounts Receivable Revenue Expense Profit Cash Accounts Receivable Cash Accounting $200 $100 $100 $100 Month 1 Accrual Accounting $200 $100 $100 $100 Month 2 Cash Accounting Accrual Accounting $0 $200 $100 $100 -$100 $100 -$100 -$100 $200 Month 2 Income Statement Line Items B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n • Start with the revenues and filter down through each expense to the bottom line (net income/earnings) • Revenue • - Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) • - Operating Expenses • Research and Development • Selling, General, & Administrative (SG&A) • Depreciation & Amortization • - Other • Non-Recurring • Interest • - Taxes • = Net Income Line Items B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n Depreciation and Amortization • Depreciation refers to the allocation of the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life • Affects how you record purchasing Property, Plants, and Equipment (PP&E) • E.g. A company buys a $1,000 machine with a useful life of 10 years • The $1,000 dollars is allocated either evenly over the 10 years (straight line depreciation) or with varied deductions (Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery system [MACRS]) • Amortization is the same principle as depreciation but for intangible assets • E.g. a healthcare company spends $1,000 for a patent with a useful life of 5 years Fundamental Analysis and the Income Statement Profitability Ratios B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n 1. Gross Margin = Gross Profit ÷ Net Sales Revenue • how much profit realized per unit sold • 40250/115000=35% 2. Profit Margin Ratio = Net Income ÷ Net Sales Revenue • percent of sales revenue that becomes net income • 13725/115000=11.9% Fundamental Analysis and the Income Statement B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n Profitability Ratios • Price / Earnings Ratio (PE Ratio) • Net Income of $16.36 Billion • 58.87/(16.36/3.21)=11.55 B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n GAME TIME GUESS THAT COMPANY GILEAD SCIENCES B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n GAME TIME GUESS THAT COMPANY GENERAL MOTORS B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n GAME TIME GUESS THAT COMPANY TESLA MOTORS B U C K E Y E C A P I TA L I N V E S T O R S – I n f o r m a t i o n S e s s i o n GAME TIME GUESS THAT COMPANY J.C. Penney