Sri Lanka Public Sector Accounting Standards (SLPSAS)
advertisement

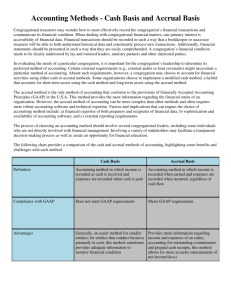
P.Ariyasena Chief Accountant Ministry of Foreign Employment Promotion and Welfare Introduction Sri Lanka Public Sector Accounting Standards (SLPSAS)were based on the International Public Sector Accounting Standards (IPSAS)published by the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) . Necessity and Purposes of SLPSAS Accounting standards are required for the purposes of maintain uniform and quality financial statements, They are intended to provide a framework and basis for improving government Accountability improved accounting and financial reporting. through It will help for decision making process by providing necessary information for resource allocation among the various Public Sector entities Public Interest How to help the Accounting Standards for maintaining Government Accountability Management is responsible for; Preparation of improved and quality financial and other reporting; Reviewing of Financial and other reports; Taking corrective action based on such reviews Purposes of quality and improved Financial Statements to Management The quality of Financial Statements are helped to maintain; For decision making process; For planning and management of public sector entities. Purposes of quality and improved Financial Statements to Stake Holders Stake holders can; Access how the accountability has discharged by the management; Access the financial and operating performance Compare one entity with other similar entity Compare one period with another period Applicability of the SLPSAS Sri Lanka Public Sector Accounting Standards apply to all public sector entities other than Government Business Enterprises (GBEs) ,which are complianced with SLASs Public Sector entities prepare FS on accrual basis of accounting Applicable for general purpose FS For Material Items Benefits of the applying of SLPSAS to the Public Sector Improved financial management and financial discipline Improved quality and reliability of financial reporting by government Improved financial and economic performance Harmonization between economic and financial reporting requirements Components of Financial Statements Statements of Financial Positions Statements of Financial Performance Cash Flow Statements Statements of Changes in Equity/Net assets Accounting Policies Notes to the FS Accrual Basis Accrual Basis means a basis of accounting under which transactions, other events and condition are recognized when they occur.(and not only when cash or its equivalent is received or paid).Thefore,the transactions and events are recorded in the accounting records and recognized in the financial statements of the periods to which they relate. The elements recognized under accrual accounting are assets,liabilities,net assets/equity, revenue and expenses. Shifting from Cash Basis to Accrual Basis Disclosure requirements in FS Applicable all SLPSAS Required transitional period Major issues arise in PPEs,Revenues ,and Liabilities Authority for SLPSAS GOSAL Financial Regulations Finance Act No 38 of 1971 ICASL