Integumentary System Review WS ans
advertisement

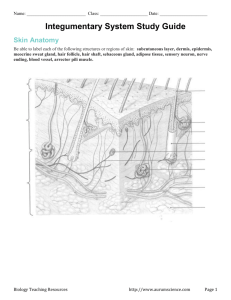
Integumentary System Review #1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The 5 Function(s) Physical protection Temperature Regulation Protects against water loss Excretion Synthesis of vitamin D3 #2 and #3 Serous, Mucous and Synovial Membranes • Serous: line body cavities with no openings (thorax) • Mucous: line cavities that open to outside (anus, nose) • Synovial: line joints (elbow) #4 Structure of Skin 2 layers – epidermis and dermis #5 Which layer has the most accessories? The Dermis #6 • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Epidermis Layers from outer to inner Stratum Corneum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Spinosum Stratum Basale #7 Melanocytes in the Stratum Basale produce melanin #8 Skin Color • 1. 2. 3. Is determined by 3 pigments Hemoglobin – red pigment within rbc Melanin – brown pigment in melanocytes Carotene – orange-yellow pigment found in both epidermal cells and dermal fat cells #9 Dermis contains... • 1. Elastic and fibrous connective tissue • 2. Blood vessels integrated within to help regulate body temperature • 3. Nerve tissue carries sensory impulese • 4. Hair follicles • 5. Sebaceous Glands (oil) • 6. Sweat glands #10 Subcutaneous contains... • 1. Adipose tissue (insulation) • 2. Larger blood vessels • 3. Larger nerve fibers #11 Accessory Structures of the Integument 1. Hair follicles 2. Oil and sweat glands 3. Nails #12 Hair • Most skin surfaces • Composed of recycled epidermal cells • Arrector pilli muscle controls “goosebumps” • Hair color is genetic #13 & #14 Sebaceous Glands • Attached to hair follicles (usually) • Secrete oil which helps keep hair soft & waterproof • Acne is a bacterial infection of the sebaceous gland #15 Sweat Glands • Most numerous in palms & soles • Sweat is mostly water, but also salts and urea and uric acid. • Some are specialized such as the ones in the ear (ear wax) • Response to heat or emotional stress #16 &17 Regulation of Body Temperature • 37°C or 98.6°F • Heat Lost = Heat Produced • Thermometer is called the hypothalamus (in the brain) • Internal regulation is called homeostasis (biological balance) • Sweating, shivering, flushing, are examples of temperature regulation Homework Worksheet Review Body Membranes • 1. • 2. • 3. • 4. Cutaneous Synovial Mucous Serous Functions of Integumentary System • 1. • 2. • 3. • 4. • 5. Protection Thermoregulation Excretion Keeps water in or out Vitamin D Synthesis Structure of the Skin • 1. • 2. • 3. • 4. • 5. • 6. • 7. Subcutaneous Layer Stratum Basale Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous Layer Epidermis Stratum Corneum • • • • • • • • … Structure of the Skin 8. Dermis 9. Stratum Basale 10. Stratum Corneum 11. Subcutaneous Layer 12. Dermis 13. Dermis 14. Epidermis 15. Dermis Skin Color • • • • • • • 1. Melanin, Carotene, Hemoglobin 2. Melanin 3. Melanin 4. Melanocytes 5. Sunlight 6. Genetics 7. Sun Summer tans are temporary • Because skin is continually sloughed off and new cells are formed Diagram of the Skin • • • • • • • • 13 Arrector Pili 11 Capillary 2 Dermis 8 Dermal papilla 1 Epidermis 14 Hair Follicle 4 hair Shaft 16 Nerve Fiber 12 Sebaceous Gland 9 Stratum Basale 5 Stratum Corneum 3 Subcutaneous 15 Sweat Gland 7 Sweat Gland Duct 6 Sweat Pore 10 Touch Receptor Accessory Structures • • • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Hair Follicle Sebaceous Gland Arrector Pili Sweat / Sudoriferous Apocrine Apocrine / Sebaceous Sudoriferous ….Accessory Structures • • • • • • 8. Keratin 9. Protection 10. Perspiration 11. Sebum 12. Cerumen 13. Pink Temperature Regulation • • • • • • 1. 37°C 2. 98.6°F 3. Respiration 4. Muscle 5. Hypothalamus 6. Skin …Temperature Regulation • • • • 7. Blood 8. Perspiration 9. Loss 10. Heat …. Temperature Regulation • • • • • 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Increased Flushing Sweat Evaporation Heat