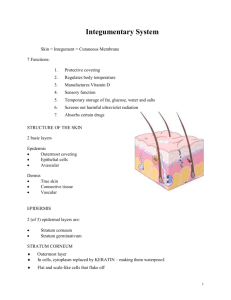
Skin - integument, cutaneous membrane
advertisement

Skin - integument, cutaneous membrane Regulate body temperature Blood reservoir Protect from external environment Sensation to stimuli Excretion & absorption Vitamin D synthesis Epidermis - outer epithelium Keratinocytes - horn-like, tough cells to protect. Melanocytes - protect from UV exposure, responsible for tanning. Dermis - deeper, germinal connective tissue Hypodermis - not skin tissue Areolar & adipose tissue Epidermal layers Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum Dermis Dermal papillae - undulating upper portion of dermis Meissner corpuscles - touch receptors Free nerve endings - hot/cold, pain, tickle, itch. Photodamage UVB can damage DNA in epidermal cells, resulting in skin cancer. Tanning is a response to tissue damage as melanin granules spread from clumps to cover more cells. Skin color - normally translucent, color determined by melanin, carotene, & hemoglobin. Melanin - amount determines skin tone. May collect as freckles or liver spots. Carotene - yellow/orange pigment in stratum corneum & fat. Hemoglobin - red pigment in blood that causes white people to appear pink. Albinism - absence of melanin Vitiligo - loss of melanocytes in patches = white spots. Cyanosis - "blue" color to the skin due to oxygen depletion. Jaundice - "yellow" skin color due to bilirubin in the blood from impaired liver function. Erythema - "red" skin due to flooded capillaries from heat, infection, infection, or allergic reaction.