Chapter 6 notes
advertisement

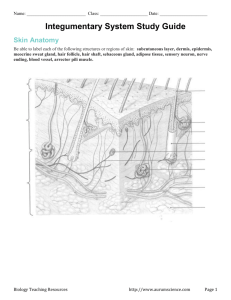
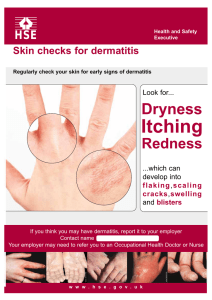
Chapter 6: The Integumentary System •skin is the largest organ Two layers of the skin: Epidermis: surface layer Dermis: deep layer -hypodermis A. Epidermis: - stratified squamous - avascular - 4-5 layers deep 1. stratum germinativum (basal layer) -firmly attached to dermis -consists mostly of -melanocytes 2. stratum spinosum (spiney layer) -melanin granules present here -Langerhans cells 3. stratum granulosum (granular layer) -thin zone 4. stratum lucidum (clear layer) -consists of a few rows of flattened dead keratinocytes -present only 5. stratum corneum (horny layer) -outermost layer; protect against abrasion and penetration - thickest layer (even thicker in areas of increased friction) -accounts for 3/4 of the epidermal thickness B. Dermis cells found here are those typically found in connective tissue gel-like matrix heavily embedded w/ collagen, elastin, & reticular fibers dermis is your "hide" richly supplied with epidermal ridges on ventral surface of hands & feet along with dermal papillae arranged in patterns create -cleavage or tension lines in the skin -stretch marks -blister: Box 6-1 Thick and Thin skin Subcutaneous Layer (hypodermis) Sebaceous (Oil) glands Sebum Sebaceous follicles Sweat (Sudoriferous) Glands: - distributed all over the skin Eccrine Apocrine Ceruminous Hair: only hairless skin is found primary function is hair grows as result of mitotic activity of epidermal cells at the bottom of the hair follicle hair growth is cyclic follicles extend from dermis --> epidermis root shaft: hair color determined by melanin arrector pili: smooth muscle Nails: Thick, heavy keratinized cells Regions cuticle: lunula: Functions of the skin: 1. Protection - chemical - physical - biological 2. Body Temperature Regulation vasodilate vasoconstrict 3. Cutaneous sensations 4. Metabolic, Storage & Secretion functions Insensible vs. sensible perspiration Observance of the Skin Color Pigment o Melanin and Carotene o Albinism Quantity of blood circulating near the surface Composition of circulating blood Discoloration o Pallor is o Flushing is o Cyanosis is o Jaundice is Various disease states will cause this discoloration Lesions – changes in skin structure Surface Lesions are often called rashes, unless raised These lesions may be local or general Accompanied by erythema Macule – Papule – Vesicle – Pustule – Deep lesions may develop from a surface lesion or from trauma Exscoriation - Laceration – Ulcer – Fissure – Burns and Grafts 1st degree – Partial thickness (superficial) 2nd degree - Partial thickness (deep) 3rd degree – Full-thickness Rule of nines – Sunburn – (Box 6-3) Tissue Response to Injury and Tissue Repair: First phase - Inflammation: short term (acute) inflammation has 4 symptoms: 1. 2. 3. 4. Initial insult causes release of chemicals from White Blood Cells these chemicals cause 1. regeneration: 2. fibrosis: scar tissue Wound healing is affected by: o Nutrition o Blood Supply o Infection o Age Aging and the Integument 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Skin Disorders Dermatology is the study of Dermatitis Contact dermatitis Eczema Diaper Rash Urticaria Seborrheic dermatitis Psoriasis Acne and Skin Infections Acne – most common form is acne vulgaris Impetigo Viral Infections Fever blisters Chicken pox Shingles Warts Ulcers Fungi Athlete’s foot Candidiasis Alopecia (baldness) Alopecia areata (immune disorder) – may affect either gender Treatment of Skin Disorders Transdermal administration Surgical removal, destroying cells (cryotherapy or laser/electrosurgery), or skin grafts (large areas) Chemotherapy (anti-inflammatory drugs) Tumors o Melanomas A B C D Pathologists specialize in the study of disease process Use of biopsies DysplasiaMetaplasiaAnaplasiaOncologists specialize in the identification and treatment of cancers Classify cancers according to appearance and site of origin o Carcinoma, Sarcoma, Leukemia, Gliomas Goal of treatment is to achieve Treatment includes 1. Surgical removal or destruction of individual tumors 2. Killing metastatic cells throughout the body