Digestive system
advertisement

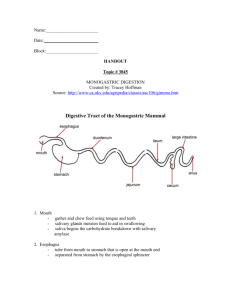
Digestive system Learning objectives To outline the digestive system and metabolism. To identify the source of energy. To describe the process of digestion and absorption of food. To describe energy conversion. Learning objectives To describe the storage of energy. To define metabolic rate. To describe energy balance of human body. To stat the metabolic rate of the liver. Human’s Nutrition Ingestion Digestion Absorption Assimilation Egestion Ingestion The process of food intake Chewing : Teeth ~ Incisor, canine, premolar & molar Tongue Mouth Swallowing Digestion Mechanical( mastication & peristalsis) + Chemical process solid food smaller pieces large molecule smaller molecules soluble forms simple ones Processes of digestion Mouth: teeth, saliva Food Oesophagus: peristalsis Stomach: gastric juice Digested food Intestine: intestinal juice Digestion in Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion ~ chewing Chemical digestion ~ salivary amylase ( Starch maltose) ~ lysozyme ( Pathogenic microbes) ~ Salts ( provide alkaline condition) ~ Mucus ( lubrication) Swallowing Digestion in stomach Mechanical ( peristalsis) Chemical ( gastric juice) ~ Pepsin (protein polypeptides) ~ Renin ( coagulate casinogen) ~ HCl activator kills or inhibit bacterial growth stimulates gastric secretion ~ Mucus ( lubrication) Digestion in small intestine I Duodenum (25cm) + Jejunum(2.5m) + ileum (3.6m) Bile ~ produced by liver ~ contain no enzyme ~ Sodium bicarbonate, bile salts, bile pigments Digestion in small intestine II Pancreatic juice ~ produced by pancreas ~ sodium bicarbonate ~ enzymes amylase lipase trysinogen nuclease Digestion in small intestine III Intestinal juice ~ produced in the intestinal wall ~ alkaline mucus ~ enzymes maltase amylase sucrase peptidase lactase Digestion in small intestine IV Mechanical ~ the chyme is mixed with intestinal juices by intestinal movement. Peristalsis- rhythmic contraction & relaxation of gut wall Dividing movement Absorption No absorption in mouth & oesophagus Absorption of alcohol & water in stomach Absorption in small & large intestine Adaptation for absorption in small intestine Thin surface ~ easier to pass through Transport vessels ~ current of blood Great surface area ~ numerous finger-like cilli & microvilli Absorption via blood vessels Amino acids. Monosaccharides, water soluble vitamins, salts & water Carbohydrates ~ galactose >glucose >fructose ~ by active transport Amino acids ~ by active transport vitamins & mineral water ~ by osmosis Absorption via lacteal Glycerines, fatty acids &fat soluble vitamins Absorbed through epithelial cell into the lymphatic ducts superior vena cava Heart Different parts of body Absorption in large intestine Water & mineral salts excess water, nutrients & undigested materials faeces Others bacteria ~ produces Vitamin B & K as byproducts Diarrhoea & Constipation Assimilation of food Carbohydrate ~ mainly glucose ~ as chief energy source ~ excess glucose converted into glycogen & subcutaneous fat Amino acids ~ synthesis protein ~ excess not stored but deaminated ~ Amino acid urea+CO2 Fats ~ as energy source ~ as structural substances ~ secreted as oil ~ excess stored as adipose tissues Function of liver Regulation ~ glucose glycogen ~ amino acid urea+CO2 ~ Fat & oil glycogen Production ~ Heat ~Bile ~Cholesterol ~ Red blood cells Storage ~ blood & vitamins Elimination of hemoglobin Detoxification Homeostasis ~ blood clotting Defense ~ phagocyte cells Pancreas It is a mixed gland consisting of exocrine and endocrine tissues; It is an elongated gland lying in the loop formed by duodenum and the under surface of stomach. Function of pancreas Exocrine secretion: ~ pancreatic juice ( amylase, maltose, trypsin) Endocrine secretion ~ insulin: glucose in blood glycogen in liver; blood glucose level lacking of insulin: Diabetes mellitus ~ glucagons: glycogen in liver glucose in blood blood glucose level Balanced diet It is a diet contains all the essential nutrients in the correct proportion so as to provide enough energy, mineral salts and vitamins for regulation and protection. Component of a balanced diet Carbohydrate (55%) Lipid (<30%) Protein (15-20%) Water Roughage Mineral salt and vitamin