Digestive System Vocabulary: Key Terms & Definitions
advertisement

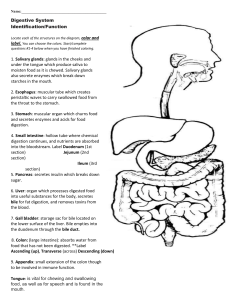
Digestive Vocabulary Mechanical Digestion- when foods are physically broken down into smaller pieces (physical change) Chemical Digestion- chemicals produced by the body break foods into their smaller chemical building blocks/ molecules (chemical change) Absorption- process by which nutrients pass through the walls of the digestive system and enter the blood stream Saliva- fluid produced in the salivary gland and released in the mouth to aid in digestion Enzyme- proteins that speed up chemical reactions in the body Epiglottis- flap of tissue that blocks the trachea, stopping food from entering the lungs Esophagus- muscular tube that leads from the mouth to the stomach Peristalsis- involuntary waves of muscle contractions that pushes food through the digestive system Stomach- the j-shaped pouch that is made of smooth muscle; mostly mechanical digestion and some chemical digestion Liver- largest organ in the body; produces bile, breaks down medicine, filters toxins, and regulates blood sugar level Bile- substance produced by the liver that breaks up fat particles into smaller pieces (mechanical digestion) Gall BladderPancreas- stores bile and releases it into the small intestine produces enzymes that are released into the s. intestine that break down fat, starch, and protein; makes insulin Villus (villi)- located on surface lining of small intestine; responsible for absorption Large Intestine- where water is absorbed into the bloodstream; bacteria lives here and produces vitamin K and gas Rectum- tube where wastes are stored Anus- the opening where waste is eliminated from the body Teeth- rip, tear, crush food in the mouth; mechanical digestion TongueDuodenum- muscle in the mouth that aids in chewing and swallowing first part of the small intestine where bile, from the gall bladder, and enzymes, from the pancreas, enter