Power Point Ch 5
advertisement

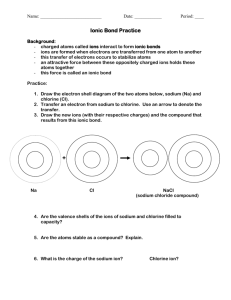
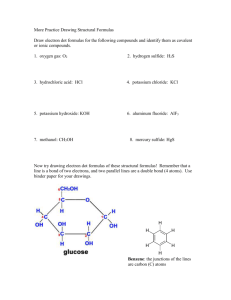
CHAPTER 5 IONIC COMPOUNDS Mrs. Czyryca What you already know: Ionic compounds donate and accept electrons, not share, in order to become stable. Ionic compounds consist of a metal and a nonmetal. An atom that has lost an electron has a positive charge. An atom that has gained an electron has a negative charge. Remember my joke? Two atoms were walking down the street. Looking all around, one says, “Oh my gosh, I lost an electron!” The other says, “Are you sure?!” The first says, “I’m POSITIVE!” You should also remember: When a compound forms and it’s atoms become stable, energy is given off. And that’s EXOTHERMIC! We are using a new unit for ionic compounds Instead of using atoms, molecules, particles, or ions as a unit---we will use FORMULA UNITS Formula units are the smallest collection of an ionic compound For example: Instead of writing: 6.022 x 1023molecules NaCl Write: 6.022 x 1023 formula units NaCl Formation of KCl from it’s elements As you can see from the prior slide, KCl doesn’t exist as a molecule. There are many, many K and Cl atoms bonded into a structure called the CRYSTAL LATTICE. The gaseous chlorine, Cl2, exists as individual molecules. The metal, potassium atoms, K, just pile up like oranges at the grocery store. Look again… Let’s look individually at the potassium and chlorine atoms. K is in group 1 on the periodic table… So what is it’s charge likely to be once it loses an electron to become stable? +1 Chlorine is in group 17 What charge would chlorine have once it gains an electron in order to become stable? -1 What are the positive ions called? Cations That’s pronounced “cat” – “ion” What are the negative ions called? Anions That’s pronounced “an” – “ion” not ant ion, an’ ion! We know a positive with a negative =zero That’s electroneutrality! when the charges equal zero +1 -1 = 0 (can I use a calculator?) How many cations and anions are present in MgCl2? MgCl2? Just one cation. And two anions How many cations and anions are present in MgCO3? MgCO3? Just one cation still. And one anion- carbonate One more… How many cations and anions are present in Mg3(PO4)2? Mg3(PO4)2? Three cations. And two anions- two phosphate polyatomic anions Potassium’s electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 It loses that electron in the 4s orbital to become stable. It then has the same electron configuration as a noble gas. VERY STABLE! ISOELECTRONIC having the same electron configuration as another element The potassium ion is isoelectronic with Argon. 1s22s22p63s23p6 chlorine’s electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p5 It gains an electron in the 3p orbital to become stable. It then has the same electron configuration as a noble gas. VERY STABLE! ISOELECTRONIC having the same electron configuration as another element The chlorine ion is also isoelectronic with Argon. 1s22s22p63s23p6 Naming ions (atoms with a charge) Like any cation, the potassium keeps it’s name and you add the word “ion” to the end. “Potassium ion” Not too tricky, huh? Naming ions (atoms with a charge) Like any anion, the end of chlorine changes to “ide” and you add the word “ion” to the end. Chloride ion What does a roman numeral tell us? The charge on the cation Never an option for the anion b/c it only has one possible charge EVER!