Lecture 8
advertisement

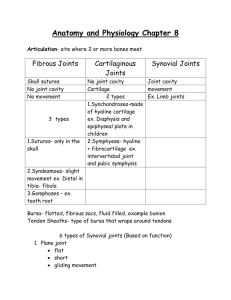
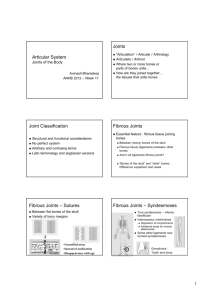
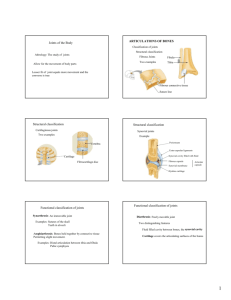
Lecture 8: Articulations (Joints) I. Classification by Function A. synarthroses - immoveable (sutures in cranium) B. amphiarthroses - slightly moveable (tibia-fibula) C. diarthroses - freely moveable (shoulder joint) II. Fibrous Joints A. Sutures 1. between cranial bones 2. very tight, thin layer of connective tissue 3. synostoses - bone replaces connective in adult B. Syndesmoses 1. very little freedom for movement 2. interosseous membrane/ligament present C. Gomphoses 1. one part fit tightly into the other 2. periodontal tissue holds parts firmly together 3. example: teeth in the mandible and maxillae III. Cartilaginous Joints A. Synchondrosis 1. hyaline cartilage --> bone over time 2. example: area between epiphysis & diaphysis of bone 3. example: joint between ribs and sternum B. Symphysis 1. bones connected by disc of fibrocartilage 2. allows for slight movement (amphiarthrotic) 3. example: pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs IV. Synovial Joints A. Structure 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. any joint where there is a space between bones synovial cavity - space between the bones freely moveable joints (diarthrotic) articular cartilage - covers articular surface articular capsule - encloses the cavity itself a. fibrous capsule - attached to periosteum i. ligaments - clearly defined connections b. synovial membrane - inner layer of capsule 1 i. produces synovial fluid ii. reduces friction in the joint 6. accessory ligaments - additional support a. extracapsular - outside capsule b. intracapsular - within capsule 7. articular discs (menisci) - pads between bones 8. bursae - sac-like structures that reduce friction a. between tendons, muscle, ligaments: and bone B. Factors that Limit Movement in a Joint 1. 2. 3. 4. "fit" between the articulating bones tension of the ligaments arrangement and tension of the muscles opposition of muscles restricting range of motion C. Types of Movements in the Joint limb 1. gliding - one bone slides over another (carpals) 2. angular motion - change the angle between bones a. flexion - decrease the angle b. extension - increase the angle c. abduction - away from the midline d. adduction - toward the midline 3. rotation - circular motion of the long axis 4. circumduction - distal end moves in a circle 5. inversion - sole of foot moves medially 6. eversion - sole of the foot moves laterally 7. dorsiflexion - raising foot toward lower limb 8. plantar flexion - extending foot away from lower 9. protraction - forward in the horizontal plane 10. retraction - backward in the horizontal plane 11. pronation - radius "radiates" over the ulna 12. supination - forearm returns to anatomical position 13. elevation - upward motion, in a superior direction 14. depression - downward motion, inferior direction D. Types of Synovial Joints 1. gliding joints (arthrodia) (nonaxial) a. side-to-side; back-and forth in grinding manner b. carpals, tarsals, scapula-clavicle 2. hinge joints (ginglymus) (monaxial) a. movement occurs in a single plane b. elbow, ankle, interphalangeal 3. pivot joints (trochoid) (monaxial) a. rotation around another bone b. atlas-axis (C1-C2), proximal radius-ulna 4. ellipsoidal joints (condyloid) (biaxial) a. side-to side; back-and-forth in smooth manner b. radius-carpal joint in the wrist 5. saddle joints (sellaris) (biaxial) a. one bone "sits" in the saddle of another b. trapezium-thumb metacarpal joint 6. ball-and-socket joints (spheroid) (triaxial) 2 a. works just like a joy-stick in all directions b. humero-scapular joint; coxal (hip) joint V. Examples of Major Articulations (Joints) A. Humeroscapular Joint (Shoulder) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. head of humerus <--> glenoid cavity of scapula ball-and-socket joint articular capsule - surrounds entire joint coracohumeral ligament glenohumeral ligaments transverse humeral ligament glenoid labrum - fibrocartilage around glenoid fossa bursae of the shoulder a. subscapular, deltoid, acromial, coracoid B. Femorocoxal Joint (Hip) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. head of femur <--> acetabulum of coxal bone ball-and-socket joint articular capsule -surrounds entire joint iliofemoral ligament pubofemoral ligament ischiofemoral ligament capitate ligament - acetabulum --> head of femur acetabular ligament - fibrocartilage around acetab. transverse ligament of acetabulum C. Tibiofemoral Joint (Knee) 1. Three Joints in One a. patellofemoral joint b. medial tibiofemoral joint c. lateral tibiofibular joint 2. articular capsule 3. ligaments: patellar, oblique popliteal, arcuate popliteal, tibial collateral, fibular collateral 4. intraarticular ligaments a. anterior cruciate ligaments b. posterior cruciate ligaments 5. articular discs a. medial meniscus b. lateral meniscus 6. bursae: anterior, medial, lateral 3