Respiratory Physiology - IU School of Medicine
advertisement

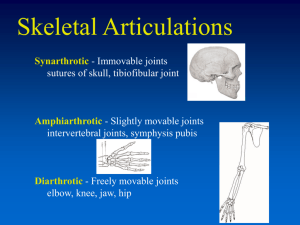
Ernest F. Talarico, Jr., Ph.D., M.S., B.S., C.L.A. Assistant Director of Medical Education Assistant Professor of Anatomy & Cell Biology Course Director, Human Gross Anatomy & Embryology Indiana University School of Medicine - Northwest Gary, Indiana Objectives Articulations Pathology of Articulations The Knee Joint The Hip Joint Radiographs of the joints Photographs of actual human bones Photographs of human cadavers NWCME 2003 - 2 Articulations An articulation is a place of union between two or more bones (i.e., a joint) classified according to the manner or type of material by which the articulating bones are united fibrous joints (united by fibrous tissue) cartilaginous joints (hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage) synovial joints (most common; fluid filled capsule) NWCME 2003 - 3 Synovial Joint most common type of joint and the most complex provide free movement between bones three distinguishing features united by fibrous tissue amount of movement depends on fiber length primary cartilaginous joints are usually temporary unions, such as those present during development of long bones (i.e., they permit growth in length) secondary cartilaginous joints are strong, slightly moveable joints NWCME 2003 - 4 Pathology Fractures Rheumatoid Arthritis Osteoarthritis NWCME 2003 - 5 Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) A Chronic Inflammatory Disorder 1% of the world’s population is affected by RA, females 5X more often than males principally attacks joints, but may affect many tissues and organs exact cause is unknown, but RA is believed to be triggered by exposure of a susceptible host to an arthritogenic antigen leading to a continuing autoimmune reaction NWCME 2003 - 6 Osteoarthritis Degenerative Joint Disease most common type of joint disease; affects 90% of individuals by age 65 progressive erosion of articular cartilage intrinsic disease of cartilage in which biochemical and metabolic alterations result in its breakdown NWCME 2003 - 7 General Information Hip Joint a multiaxial ball-and-socket type of synovial joint • • • • extension and flexion abduction and adduction medial and lateral rotation circumduction designed for stability as well as for a wide range of movements • next to the shoulder joint, it is the most stable • weight bearing reinforced by ligaments and muscles NWCME 2003 - 9 Bones of the Hip Joint pelvic bone femur (thighNWCME bone)2003 - 10 NWCME 2003 - 11 NWCME 2003 - 12 iliofemoral ligament (horizontal) iliofemoral ligament (vertical) pubofemoral ligament iliofemoral ligament (horizontal) ischiofemoral ligament NWCME 2003 - 13 zona orbicularis Ligament of the Head of the Femur Ligamentum capitus femoris NWCME 2003 - 14 NWCME 2003 - 15 NWCME 2003 - 16 Osteoarthritis Histopathology progressive erosion of cartilage femoral head with fibrocatilaginous plug and ebrunated bone articular surface with absence of articular cartilage; bone thickening, and subchondral bone cyst Rx. (1) exercise; (2) weight loss; (3) joint replacement NWCME 2003 - 17 Hip Replacement Surgery AML® Total Hip System • the first porous-coated implant indicated for use without cement • designed for use with DePuy's patented Porocoat® Porous Coating The S-ROM® Total Hip System • a primary hip system with more than 15 years of clinical success • it is the number one modular stem worldwide. NWCME 2003 - 18 General Information Knee Joint a hinge type of synovial joint • extension and flexion • hinge movements are combined with gliding and rolling, and with some rotation about a vertical axis • most complex joint of the human body consists of 3 articulations • lateral and medial articulation between the femoral and tibial condyles • intermediate articulation between the patella and femur reinforced by ligaments • commonly impaired when hyperextended NWCME 2003 - 20 Bones of the Knee Joint patella femur tibia The fibula plays no role in the knee. NWCME 2003 - 21 NWCME 2003 - 22 Views of the Knee Joint NWCME 2003 - 23 NWCME 2003 - 24 Patellar Ligaments of the Knee Extracapsular Ligaments Fibular Collateral Tibial Collateral Oblique Popliteal Arcuate Popliteal NWCME 2003 - 25 Oblique Popliteal Arcuate Popliteal * * NWCME 2003 - 26 Ligaments of the Knee Intra-articular Ligaments Cruciate Ligaments (ACL and PCL) Menisci (lateral & medial) NWCME 2003 - 27 NWCME 2003 - 28 Bursa of the Knee Joint NWCME 2003 - 29 “Unhappy Triad” of Knee Injuries (1) (2) (3) tibial collateral ligament ruptures, opening the joint on the medial side tearing of the medial meniscus snapping of the ACL NWCME 2003 - 30 Rheumatoid Arthritis Histopathology females > males principally attacks joints, but may affect many tissues and organs swelling of metacarpal phalangeal joints ulnar deviation of fingers NWCME 2003 - 31 Rheumatoid Arthritis Histopathology hyperplastic synovium lymphoid follicles and villous folds inflammation nodules with central necrosis and inflammatory infiltrate Rx. (1) anti-inflammatory agents; (2) remission-inducing drugs; (3) immunosuppressive drugs; (4) surgery NWCME 2003 - 32 Knee Replacement Surgery LCS® Knee • developed more than 20 years ago • is a patented, one-of-a-kind knee system because its mobilebearings offers a wide range of options to allow the surgeon to match the implant to the patients' anatomy The P.F.C.® Sigma Total Knee System • is the leading fixed-bearing knee system in the world • the recent addition of the P.F.C. Sigma Rotating Platform results in a comprehensive implant system that provides a choice between fixed or mobile-bearings, intraoperatively NWCME 2003 - 33 NWCME 2003 - 34 Acknowledgements Thomas J. Scully Orthopaedic Consultant Sales Associate & Cadaver Prosector Daniel Auger, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Knee Research & Development DePuy® Orthopaedics, Inc. a Johnson & Johnson Company NWCME 2003 - 35 The human cadaver donors, who bequeathed their bodies for medical education and research and who permitted the anatomical photographs shown in this presentation. NWCME 2003 - 36