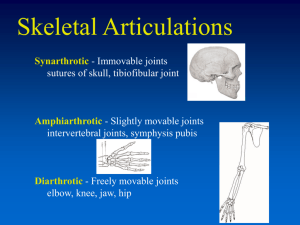
Clinical Applications
advertisement

1 Possible Clinical Application Questions for Exam 1 1. Gastroenterologists use X-rays to check for ulcers or other stomach and upper digestive tract disorders. Before the X-rays are taken why is it necessary for the patient to drink large quantities of a solution that contains barium ions? Barium is very radiodense, and the contours of the gastric and intestinal lining can be seen against the white of the barium solution. 2. A patient reports stabbing pains in the right hypochondriac region. Based on your knowledge of the organs in this area give a probable diagnosis? The right hypochondriac region contains the gallbladder and a larger portion of the liver. Initial diagnosis would be gallstones. 3. Mikhail has been diagnosed with a ruptured appendix, which has allowed bacteria from his intestinal tract to infect his peritoneum. Why is this condition (peritonitis) so dangerous? The peritoneum, the largest serous membrane in the body, covers most organs in the abdominal cavity. Therefore, an infection in this structure can spread to any or all organs in the cavity. 4. Your friend tells you that he is taking the antibiotic streptomycin for an infection. He wants to know how this particular antibiotic can kill bacterial cells but not kill his own cells. What is your explanation? Streptomycin inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by interfering with ribosomal function of bacteria and has no effect on the ribosomes of humans. If the bacterial are unable to synthesize new protein (many of which would be essential enzymes), they will die. 5. You over hear a group of teenagers betting each other as to who could drink the most water within a 30 minute time span. Being the excellent medical student that you are you interrupt them and explain the dangers of drinking seemingly harmless liquid (water) in such a short period of time. What is your explanation? Drinking water is hypotonic to the cells of your body. Taking in too much water in a short period of time will cause the blood and eventually the interstitial fluid to become hypotonic to the body cells. The extracellular water then moves by osmosis into the body cells and cause them to rupture. This could, and has in the past, kill a person. 6. Some pediatricians recommend the use of a 10% salt solution to relieve congestion for infants with stuffy noses. What effect would such a solution have on the cell lining the nasal cavity, and why? The 10% salt solution would be hypertonic with respect to the cells lining the nasal cavity, because this solution contains a higher concentration of salt than do the cells. The hypertonic solution would draw water out of the cells, causing the cells to shrink and adding water to the mucus, thus relieving the congestion. 2 7. In a hospital, a nurse gave a patient recovering from surgery a transfusion of 5% salt solution by mistake instead of a transfusion of physiological saline (0.9% salt). The patient quickly went into shock and soon after died. What caused the patient to enter into a state of shock and die? Because of the increase of solute concentration in the body fluid, it became hypertonic to the RBCs. The RBCs dehydrated and shrank – crenation. The crenated RBCs lost their oxygen-carrying capacity and the body tissues were deprived of the oxygen necessary of cellular metabolism to support life. 8. Vitamin C is important to maintain health. What relationship does vitamin C have to tissue development in the body? Vitamin C is required by key enzymatic reactions for proper collagen formation. Collagen is a protein substance that forms the framework of connective tissue. The connective tissue is the building material for bones, cartilage, teeth, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels. Without the proper production of collagen many body systems are affected. Lack of vitamin C can cause the condition known as scurvy. 9. The knee joint is quite susceptible to injury involving the tearing of cartilage pads within the knee joint. In most cases, why is surgery needed? Cartilage heals poorly and in many instance does not heal or recover at all after a severe injury. Cartilage is avascular, because chondrocytes produce a chemical that discourages the formation of blood vessels. This property makes nutrient and oxygen delivery difficult. Also the chondrocytes do not readily divide. The lack of cell division and avascularity contribute to the poor healing of cartilage thus requiring surgery. 10. After many years of smoking, Mr. Butts is plagued by a hacking cough. Explain the causes of this cough. The respiratory passages are lined by ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium that contains mucus producing goblet cells. The mucus traps debris and foreign material that is moved by the beating cilia to the pharynx to be swallowed. Chronic smoking initially paralyzes the cilia, resulting in a buildup of mucus in the airways. The hot air and particulates sear and burn off the cilia, which eventually do not get replaced. The epithelium responds by producing even more mucus which cannot be moved due to the lack of cilia. The only way that the respiratory system can clear the debris and mucus is with forceful bursts of air: coughing. 11. Assuming that you had the necessary materials to perform a chemical analysis of body secretions, how could you determine whether a secretion was merocrine or apocrine? Because apocrine secretions are released by pinching off a portion of the secreting cell, you could test for the presence of cell membranes, specifically for the phospholipids in cell membranes. Merocrine secretions do not contain a portion of the secreting cell, so they would lack membrane constituents. 3 12. A clinical diagnosis has been made that substantiates the presence of a herniated disc and a severe case of sciatica. What is the relationship between the two conditions? When the nucleus pulposus (gelatinous interior) of the disc leaks through the annulus fibrosis (fibrous outer portion) of the disc, the affected disc balloons out from between the bony parts of the vertebrae. If the bulging or herniated area is large enough, it may press on a nerve, causing severe or incapacitating pain. Usually, the sciatic nerve is affected. Sciatica is generally located in the lumbar region and can radiate over the buttock, rear thigh, and calf, and can extend into the foot. 13. What is the association between the metabolic disorder known as gout, which affects the joints, and damage to the kidney? Gout is a metabolic disorder in which there is an increase in uric acid in the body with precipitation of sodium urate crystals in the kidneys and joint capsules. The presence of uric acid crystals in the joints can lead to an inflammatory response in the joints. Usually the great toe and other foot and leg joints are affected, and kidney damage from crystal formation occurs in more advanced cases. 14. A high school football player notices swelling in the knee joint. He decides he’d better tell the coach who responds by telling him, “You have water on the knee”. As a student of anatomy, explain what the coach is talking about. Diarthroses, or synovial joints such as the knee joint, contain small pockets of synovial fluid which are called bursae. The “water on the knee” is the synovial fluid that has been released from the bursae due to ligament damage in or around the joint capsule. The synovial fluid leaks out of the bursa and fills the cavities in and around the region of the knee. 15. Steve injured his right knee during a basketball game when he jumped to rebound the ball and landed off-balance on the right leg. He has been experiencing pain and limited mobility of the knee joint. What type of injury do you think Steve has? What techniques would be used to explore the extent of the damage? Steve probably tore the medial meniscus. This is the most common knee injury and is caused by the lateral surface of the lower leg being forced medially. The torn cartilage is painful, usually restricts joint mobility, and may lead to chronic problems. It is possible to examine the interior of a joint without major surgery, by using an arthroscope. An arthroscope uses fiber optics – thin threads of glass or plastic that conducts light – to investigate inside a joint, and if necessary perform surgical modification at that time (arthroscopic surgery). A totally non-invasive method of examination is MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).