Intro to Anatomy note sheet
advertisement

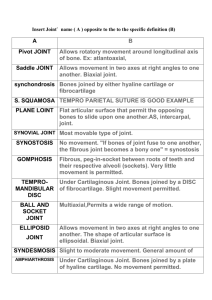
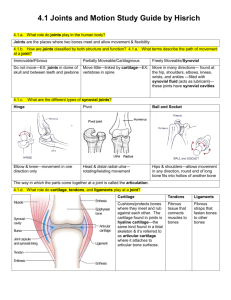
Introduction to Anatomy Understanding Anatomy It’s the_________________ of many health care professions An ATC needs to have an excellent ____________ of anatomy in order to _____________ what structures have been injured They also need to understand what constitutes ________________ movements in order to design appropriated __________________ and strength conditioning programs Anatomical position There is a particular ______________ of the body which all medical professionals use as a _________________. Refers to an erect _________, arms at the _________, and palms facing ____________. The body ________ in relation to 3 planes Frontal Sagittal TransverseCommon Medical Terms of Location Anterior Ex. Anterior aspect of the lower leg means the front of the leg was injured ______________-refers to the back of the body Ex. If the back of the knee hurts, it’s the posterior aspect of the knee Medial –______________________ (sagittal plane) ________________-towards the outside (sagittal plane) Proximal-________________________________ (such as where the limb attaches to the trunk) Ex. The shoulder is proximal to the elbow ______________-means away from the attachment The knee is distal to the hip Superior The knee is superior to the ankle _____________-refers to one point being lower than another The pelvis is inferior to the ribs Dorsal ___________-refers to the anterior aspect of the foot or hand Superficial ___________-means away from the body’s surface Bones Bones have 3 primary ________________ Protect vital ______________ and _________________ from trauma Bones are stiff structures that are acted on by _____________ to create _____________ Bones are __________________ active; they produce ____________ cells and store _____________ **bones also protect the nerves and blood vessels that travel alongside them Skeleton Made up of approximately ______ bones and an astounding number of _____________ The skeleton is categorized into 2 parts: Axial skeleton AppendicularTypes of Bones ____________ (like the femur) At the end of each long bone is an area where growth occurs Called the ____________ (growth plate) Vulnerable to injury during ______________________ ___________(like the metacarpals) __________ (like the scapula) ______________ (like the vertebra) Cartilage Covers the ________ of long bones and can be found ____________ bones. Functions of cartilage: _________________ (example: the ribs and sternum) Absorb _________ Permit smooth bone _____________ Muscles Contractions allow the body to: **muscles produce heat as well Ligaments and Tendons Both are composed of _____________ tissue Tendons attach ___________ to __________ Transmit the force that a muscle exerts Ligaments connect ____________ Help form ________ Classification of Joints ___________________ (aka synovial joints) Consist of a _________________, synovial membrane, hyaline cartilage, and ______________ Examples are ________ joints (elbow and knee) and ____________ or ball-and-socket joints (shoulder and hip) ______________________-have cartilage attaching 2 bones together Aka cartilaginous joints Example is where the ribs __________ the sternum ______________________-held together by tough connective tissue and are basically immovable Aka fibrous joints This type of joint joins the _________ of the skull and the tibia and fibula of the lower leg Movement terminology ______________-a bending movement around a joint in a limb away from its straightened position Extension-a straightening ____________ around a joint to _________ it to anatomical position ______________-movement away from the midline of the body Adduction-movement __________the midline of the body ________________-a movement that turns the palm of the hand downward as if it were emptying a bowl of soup Supination-a movement that turns the palm of the hand ____________ as if it were holding a bowl of soup ______________-a movement that turns the sole of the foot inward, toward the midline of the body Eversion-a movement that turns the sole of the foot ___________, away from the __________ of the body _______________-movement of the scapulas away from one another Retraction-when the scapulas are moved or pulled __________ _________________-the spinning or turning movement of a bony segment around an axis Circumduction-movement of a limb in a ______________ pattern