Blood and Lymphatic Systems: Components & Function

Blood and the Lymphatic System
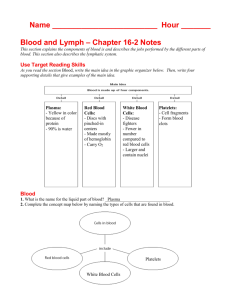
What is Blood?
• It is a type of CONNECTIVE tissue
• Contains dissolved substances and specialized cells
• The human body contains about 5 liters (1.3 gal) of blood
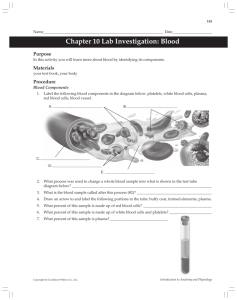
• 4 major components
PLASMA
RED BLOOD CELLS
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
PLATELETS
392 2/11/11
PLASMA
• 45% of blood is made up of cells
• 55% of blood is made up of a straw-colored fluid called
PLASMA
• Plasma is 90% water and 10% dissolved gases, nutrients, proteins, salts, waste products
392 2/11/11
Red Blood Cells
Erythrocytes
• Made from cells in the red bone marrow
• Shaped like discs with a thin center
• Contain the oxygen-carrying protein HEMOGLOBIN
• Mature red blood cells do not have nuclei
• There are 5 billion RBCs in a milliliter of blood
392 2/11/11
White Blood Cells: The First Line of Defense
• Made from cells in the bone marrow; they contain nuclei
• Function to fight INFECTION , attack bacteria and parasites
• Different types of white blood cells. Some can “eat” the attacking agent in a process called phagocytosis .
• Lymphocytes are a type of
WBC that helps create the antibody immune response.
• There are ~10 million WBCs in a milliliter of blood.
392 2/11/11
Platelets
• Fragments of cytoplasm released from bone marrow with no nuclei
• Function is to plug up cuts in the blood vessel in the process known as blood clotting .
• Release proteins into the plasma that can produce fibrin , which holds the clot together.
• There are 300 million platelets in a milliliter of blood.
392 2/11/11
Blood Clotting Thrombosis
Break in
Capillary Wall
Blood vessels injured.
Clumping of Platelets
Platelets clump at the site and release thromboplastin.
Thromboplastin converts prothrombin into thrombin..
392 2/11/11
Clot Forms
Thrombin converts fibrinogen into fibrin, which causes a clot.
The clot prevents further loss of blood..
Immunohistological Staining of a Thrombus a
Brown = platelets b
392 2/11/11
Blood Types
The Blood Types: A, B, AB, O
• Blood typing requires matching two components: an antigen and an antibody. It is an immune system.
• An antigen (or carbohydrate) is a recognition marker
• Blood types are determined by the presence or absence of two antigens – A and B – on the surface of red blood cells
• An antibody is a defensive protein made by the immune system and is present in the blood.
392 2/11/11
Blood Typing
Rh Factor is another antigen present on red blood cells. People are either Rh positive or Rh negative.
392 2/11/11
Blood Typing
Blood Type of
Donor
Blood Type of Recipient
A B AB
A
B
AB
O
Unsuccessful transfusion
O
Successful transfusion
AB blood type is a UNIVERSAL ACCEPTOR
O blood type is a UNIVERSAL DONOR
392 2/11/11
Lymphatic System
• The lymphatic system is made up of three parts:
network of vessels
nodes
organs
Its function is to collect fluid lost by blood and return fluid to the circulatory system
• The fluid is known as LYMPH
• Path: Lymphatic vessels to ducts to superior vena cava
• Lymph nodes are a filter system (bacteria)
• Lymph is moved by contractions of skeletal muscle
• Lymphatic system also moves nutrients into blood
392 2/11/11
The Lymphatic System
392 2/11/11