World History: WWI to Modern Day
advertisement

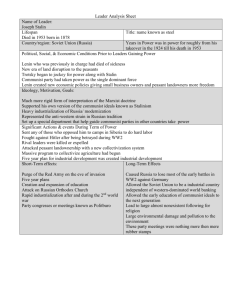
World History: WWI to Modern Day Roots of WWI World War I – “The Great War” Nationalism- The loyalty to one’s country Balkans – Ethnic groups launching revolutions against the Ottoman Empire – Some annexed by Austria-Hungary – Poland v. Russia – Ireland v. Britain Roots of WWI Militarism – Countries began building up their militaries to intimidate others Alliances – Agreements between nations to help each other in case of war The War Begins June 28, 1914- Archduke Francis Ferdinand, heir to Austria-Hungary, was assassinated by a Serbian nationalist – Austria-Hungarian/German alliance – Serbian/Russian alliance Triple Entente – Great Britain, France, Russia Central Powers – Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire The War Front Weapons – Machine guns – Poison gasses – Tanks and airplanes Stalemate develops Trench warfare – Dirty ditches – “no man’s land” in between The End and Aftermath 1917- the US enters the war 1918- the war ends when Germany is defeated – 20 million Europeans dead President Wilson wanted peace but the allies wanted to punish Germany Treaty of Versailles – Forced Germany to accept blame – Germany to pay reparations ($) Hapsburg Dynasty (ruling European family) fell Ottoman Empire- no longer existed The Aftermath Allies redrew national borders to benefit themselves New countries created causing conflict Promised independence to Arab nations but went back on their word – Mandate system Germans left resentful Laid the path for WWII League of Nations President Wilson proposed it Was meant to provide a place where countries could peacefully discuss solutions Many countries joined but no the USA Could not enforce anything Russian Revolution Czar Nicholas II- lead Russia in WWI but was overthrown in 1917 Lenin – Marxist/Communist – Bolsheviks- socialist party – Gained control of the Russian government Western nations sided with the non-communist Soviet Union= Communist Russia Joseph Stalin Became communist dictator of Russia Five Year Plan – Sought to increase industrialization in the USSR – State owned farms and starvation Purge – Stalin eliminated those he saw as a threat; some killed some sent to prisons – Murdered millions of his own people Effects of the Revolution End of the Romanov Dynasty transferring power to the lower classes Urbanization and technology Mistrust between the Russia and the west Later led to the Cold War after WWII Totalitarian v. Authoritarian Governments Democracy does not exist in either Authoritarian – Only interested in political power – Conservatives who want to preserve traditional way of life – Expects people to accept government policies and carry on with their lives Totalitarian – Government seeks to control politics, economy, culture, and social life – Terror and fear used to force citizens Italy Fascism – Nationalistic movement that is antidemocratic and anti-communist – Rules by intimidation Benito Mussolini – Used violence to settle unrest – Became dictator of Italy after gaining support from the middle class – Repressive government Adolf Hitler Took control of Germany with the Nazi Party Rose in power through Nationalism and promised of rebuilding “Third Reich” Began militarily expanding – Empire building – Appeasement Anti-Semitism-hatred of the Jewish people – “Final Solution”-called for the total elimination of the Jewish people – The Holocaust Japan Emperor Hirohito – Did not have complete control of Japanese government – Militarily controlled Hideki Tojo – Japan’s premier and led Japan through WWII Leading to War Hitler’s invasion on the Rhineland, Austria, and the Sudetenland Japan expanding in the Pacific and into China Axis Powers – Germany – Italy – Japan WWII Hitler invades Poland Britain and France enter the war Hitler takes over France Battle of Britain – Thousands of German planes bomb Britain – Winston Churchill- British prime minister – Britain holds on US Involvement US had remain neutral until December 7, 1941 attack on Pearl Harbor – US declares war Allies – United States – Britain – Soviet Union/Russia Hitler invades Soviet Union Strategy Stalin wanted US and Britain to open the western front of Europe to help him out Churchill and Roosevelt decided to attack Germany in Africa, Italy, and then the Western European Front Tehran Conference – Allies agree to invade Europe – D-day – Significance: Paved way for Western European invasion that would end the war France is won back Yalta Conference “Big Three” – Roosevelt/Truman (US) – Churchill (Britain) – Stalin (USSR) Yalta Conference – After German defeat USSR would help with Japan – Eastern European countries to get elections – USSR gets land in Poland and some in China – USSR gets most reparations because they were the hardest hit – Germany divided into four zones after the war (US, Britain, France, USSR) Significance: Laid out post-WWII Europe between the west and the communist Potsdam Conference War in Europe ended May 1945 Potsdam – Truman meets with Stalin and Churchill – Unconditional Surrender of Japan – Significance: led to the decision of the atomic bombs at Hiroshima and Nagasaki War on both fronts were finally ended Use of the atomic bombs led to the nuclear arms race between the US and the USSR – Hydrogen bomb created Post WWII Cold War – Tension b/w the US and USSR that many feared would lead to nuclear war Marshall Plan – Money given to help Western Europe’s economy and help rebuild countries Post War Japan – Created democratic government ad helped rebuild – Today a modern, industrial, and wealthy nation United Nations – Organization of different countries to find peaceful solutions to problems – Permanent Members: US, Britain, France, Russia, China Indian Independence Decolonization India was under control of Britain Mohandas Gandhi – Leader of the Indian Independence Movement – Supported non-violent protests even through beatings by the British – Unity b/w Hindus and Muslim Indians Gained independence but not religious peace Pakistan created as a Muslim state Gandhi was assassinated but inspired many China’s Communist Revolution Nationalists Mao v. Communists Zedong – Communist leader who gained control of China – USSR supported Israel Zionism- Jewish nationalism increased after the Holocaust 1948 Israel created for Jewish people Arabs upset because part of Palistine was taken Wars have broken out and still tension Latin America US was backing governments in Latin America that nationalists did not support Latin American nationalism associated itself more with the Soviet Union Cuba (Castro), Chile (Salvador Allende), Nicaragua (Sandinistas), Mexican attempt (Zapatistas) US backed anti-communist takeovers Today’s anti-US Latin American governments – Venezuela and Hugo Chavez – Bolivia and Juan Evo Morales Ayma Southeast Asia Decolonizing after WWII Many of the countries experienced unrest Vietnamese Nationalist led by Ho Chi Minh fought the French and the US – Communist nationalist won in the end Africa African nationalism also came about after decolonization Several African countries gained independence South Africa – Apartheid- official policy of racial segregation in South Africa – Nelson Mandela- arrested for his leadership for 27 years but 1994 was elected president – 1994 South African elections where black population was allowed to participate Middle East Arab National arose after the founding of Israel Abdul Nassar became president of Egypt and united Arabs in standing against the west and supporting Palestine Ethnic Conflicts African tribes fighting one another Kurds, Persians, Arabs, and Jews fighting in the Middle East Eastern Europe – Serbs, Bosnians, and Croats fighting – Serbians conquered Bosnia and began ethnic cleansing killing many Bosnians – NATO helped to maintain peace Terrorism Terrorism – Use of violence against innocent people in the name of a cause Al-Qaeda – Largest and most active terrorist group – Led by Osama bin Laden – Sept. 11, 2001 – War on Terror- invasion into Afghanistan How does this affect us today? Globalization Globalization- worldwide interdependence United Nations – Allows representatives to negotiate peacefully, provide aid, and back military forces to maintain stability World Trade Organization – Monitors countries making sure they stick to international trade agreements OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) – Several oil producing nations that control the cost and supply of oil